Bitcoin Halving - Scarcity And Value Dynamics
Explore impact of Bitcoin halving impact on supply, demand, and market dynamics. A guide to the economics of this pivotal event.
Author:James PierceReviewer:Gordon DickersonJan 30, 20241.3K Shares130.1K Views

Bitcoin halvingis a critical event in the cryptocurrency world, impacting the supply dynamics of Bitcoin and influencing its price trajectory. This phenomenon, which occurs approximately every four years, is ingrained in the Bitcoin protocol as a mechanism to control inflation and maintain the scarcity of the digital asset.
One of the most significant events on the Bitcoin blockchain is a halving, which occurs when the reward for mining is reduced in half. Since 2020, network participants that validate transactions have received 6.25 bitcoins (BTC) for each block successfully mined.
The next halving is predicted to occur in early to mid-2024, when the block reward will be reduced to 3.125. The impact of each halving will gradually fade as the block reward approaches one satoshi.
In this detailed exploration, we'll delve into the concept of Bitcoin halving, its significance, the mechanics behind it, and its historical and potential future implications.
What Is Bitcoin Halving?
Bitcoin halving, often referred to as "the halvening," is a predetermined event coded into the Bitcoin protocol that reduces the reward miners receive for validating and adding new blocks to the blockchain by half. This process occurs approximately every 210,000 blocks, which translates to roughly every four years, considering the average time it takes to mine a block.
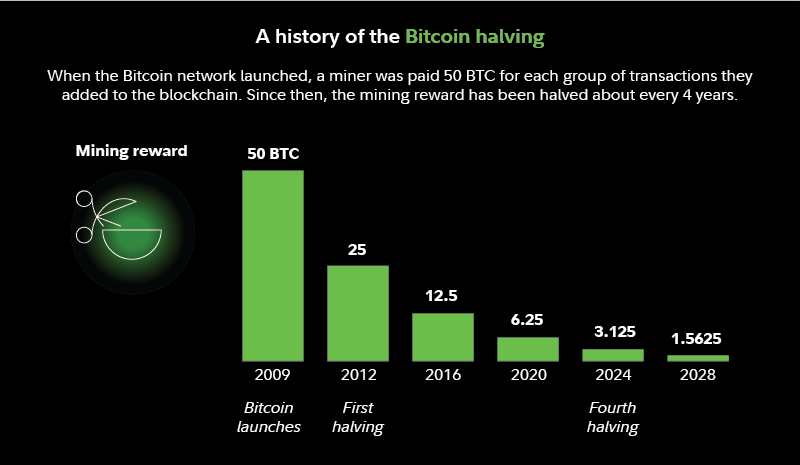
The initial block reward, when Bitcoin was launched in 2009, was 50 bitcoins per block. The first halving occurred in 2012, reducing the reward to 25 bitcoins. The second halving took place in 2016, further halving the reward to 12.5 bitcoins. The most recent halving occurred in May 2020, bringing the reward down to 6.25 bitcoins. The next halving is expected to occur in 2024.
Significance Of Bitcoin Halving
Bitcoin halving is fundamentally linked to the core principles that underpin the cryptocurrency. The total supply of bitcoins is capped at 21 million, creating a finite and scarce asset. By reducing the rate at which new bitcoins are created through halving, the system introduces a controlled and predictable inflation model.
The scarcity introduced by halving is a deliberate design choice meant to mimic precious metals like gold, where scarcity enhances value. As Bitcoin becomes scarcer with each halving, proponents argue that it can act as a hedge against inflation, making it an attractive asset for those seeking to preserve wealth over the long term.
The Mechanics Of Bitcoin Halving
Bitcoin mining is the process by which transactions are verified and added to the blockchain. Miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems, and the first one to solve the problem gets the right to add the next block to the blockchain and is rewarded with newly minted bitcoins, along with transaction fees.
During the halving event, the reward for miners is cut in half. Before the first halving, miners received 50 bitcoins for each block they successfully mined. After the first halving, this reward dropped to 25 bitcoins. Subsequent halvings further reduced the reward to 12.5 bitcoins and then 6.25 bitcoins. The process will continue until the maximum supply of 21 million bitcoins is reached.
Historical Impact Of Bitcoin Halving On Price
Bitcoin-halving events have historically been associated with significant price movements. The reduction in the rate of new bitcoin creation, coupled with growing demand, has often led to increased scarcity, fostering a bullish sentiment among investors.
In the run-up to previous halvings, there has been heightened anticipation and speculation in the market. The 2012 halving saw a significant increase in Bitcoin's price in the months that followed, and a similar pattern was observed after the 2016 halving. The 2020 halving was no exception, as Bitcoin's price experienced substantial gains in the months preceding and following the event.
However, it's essential to note that while halving events have historically been followed by bullish trends, past performance does not guarantee future results, and the cryptocurrency market is notoriously volatile.
Market Reaction To Bitcoin Halving
The market reaction to Bitcoin halving is a subject of considerable debate among analysts. Some argue that the anticipation of reduced supply and increased scarcity tends to drive up demand, leading to higher prices. Others contend that much of the impact is already priced into the market by the time the actual halving occurs.
Leading up to a halving event, there is often increased media coverage, social media discussions, and general awareness in the cryptocurrency community. This heightened attention can attract new investors and contribute to a positive feedback loop of demand.
Post-halving, the reduced rate of new Bitcoin issuance can potentially lead to a supply-demand imbalance, putting upward pressure on prices. However, external factors such as macroeconomic conditions, regulatory developments, and technological advancements also play a role in shaping market dynamics.
When Is The Next Bitcoin Halving?
Bitcoin halving occurs when a particular number of blocks have been created. Nobody knows exactly when the next halving will occur, but experts predict May 2024. That would be almost precisely four years after the previous one.
Experts believe the somewhat predictable pattern of Bitcoin halvings was intended to avoid a huge shock to the network.
However, this does not rule out a trade frenzy around Bitcoin's second halving.
“„Historically, there is a lot of Bitcoin price volatility leading up to and after a halving event. However, the price of Bitcoin typically ends up significantly higher a few months after.- Rob Chang
While many other factors influence Bitcoin's price, it appears that halving events are generally bullish for the cryptocurrency as the initial volatility subsides.
Richard Baker, CEO of TAAL Distributed Information Technologies, a miner and blockchain services provider, advises investors to be wary about the next Bitcoin halving. Although scarcity might fuel price appreciation, decreased mining activity may lead the price to plateau.
Challenges And Considerations
While many in the Bitcoin community view halving as a positive mechanism for maintaining scarcity and controlling inflation, there are critics who raise concerns. Some argue that the fixed supply model may create challenges in the long term, especially as miners increasingly rely on transaction fees to sustain their operations.
Additionally, the environmental impact of Bitcoin mining, particularly energy consumption, has been a point of contention. The halving events do not directly address these concerns, and ongoing discussions within the community revolve around finding sustainable solutions for the future.
Bitcoin Halving - FAQs
Why Does Bitcoin Have Halving Events?
Halving events are designed to control inflation, maintain scarcity, and mimic the scarcity model of precious metals like gold, making Bitcoin an attractive asset for wealth preservation.
How Does Bitcoin Halving Impact Miners?
Bitcoin halving reduces the block reward miners receive, challenging them to rely more on transaction fees for revenue as the total supply approaches its maximum of 21 million bitcoins.
How Do Investors Typically React To Bitcoin Halving?
Investors often anticipate Bitcoin halving events, leading to heightened speculation and increased demand, which can contribute to positive price movements.
Will BTC Go Up After Halving?
According to historical data, the price of bitcoin has increased following each halving event, though not immediately.
Conclusion
Bitcoin halving is a central and predetermined aspect of the cryptocurrency's economic model, designed to instill scarcity and control inflation. Its impact on the market, investor sentiment, and the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem cannot be understated.
While the historical patterns suggest a correlation between halving events and price increases, it's crucial to approach these phenomena with a nuanced understanding, recognizing that various factors contribute to the complex dynamics of the cryptocurrency market.
As Bitcoin continues to mature, its halving events will remain a focal point of attention, with their implications resonating throughout the digital asset landscape.

James Pierce
Author
James Pierce, a Finance and Crypto expert, brings over 15 years of experience to his writing. With a Master's degree in Finance from Harvard University, James's insightful articles and research papers have earned him recognition in the industry.
His expertise spans financial markets and digital currencies, making him a trusted source for analysis and commentary. James seamlessly integrates his passion for travel into his work, providing readers with a unique perspective on global finance and the digital economy.
Outside of writing, James enjoys photography, hiking, and exploring local cuisines during his travels.

Gordon Dickerson
Reviewer
Gordon Dickerson, a visionary in Crypto, NFT, and Web3, brings over 10 years of expertise in blockchain technology.
With a Bachelor's in Computer Science from MIT and a Master's from Stanford, Gordon's strategic leadership has been instrumental in shaping global blockchain adoption. His commitment to inclusivity fosters a diverse ecosystem.
In his spare time, Gordon enjoys gourmet cooking, cycling, stargazing as an amateur astronomer, and exploring non-fiction literature.
His blend of expertise, credibility, and genuine passion for innovation makes him a trusted authority in decentralized technologies, driving impactful change with a personal touch.
Latest Articles
Popular Articles