CIDR XYZ - A New Approach To IP Address Management
As the world becomes increasingly connected, the demand for IP addresses continues to grow at an exponential rate. In response, the traditional method of assigning IP addresses has become inefficient and unsustainable. To address this problem, a new approach called CIDR XYZ has been developed. Keep reading the article to explore it.
Author:Anderson PattersonReviewer:Darren McphersonMay 07, 20237.6K Shares480.6K Views
As the world becomes increasingly connected, the demand for IP addresses continues to grow at an exponential rate. In response, the traditional method of assigning IP addresses has become inefficient and unsustainable. To address this problem, a new approach called CIDR XYZhas been developed. Keep reading the article to explore it.
What Is CIDR XYZ?
CIDR XYZ is a new approach to IP address management that simplifies the process of assigning IP addresses. CIDR stands for Classless Inter-Domain Routing, which is a method of allocating IP addresses and routing Internet Protocol packets. The term "XYZ" refers to a set of unique features that differentiate this approach from traditional CIDR.
CIDR XYZ allows network administrators to allocate IP addresses more efficiently by grouping them into smaller, more manageable blocks. This approach enables more granular control over IP address allocation and helps to minimize IP address wastage.
How Does CIDR XYZ Work?
CIDR XYZ works by dividing IP addresses into smaller, more manageable blocks called CIDR blocks. Each CIDR block contains a set of IP addresses that can be allocated to devices or subnetworks.
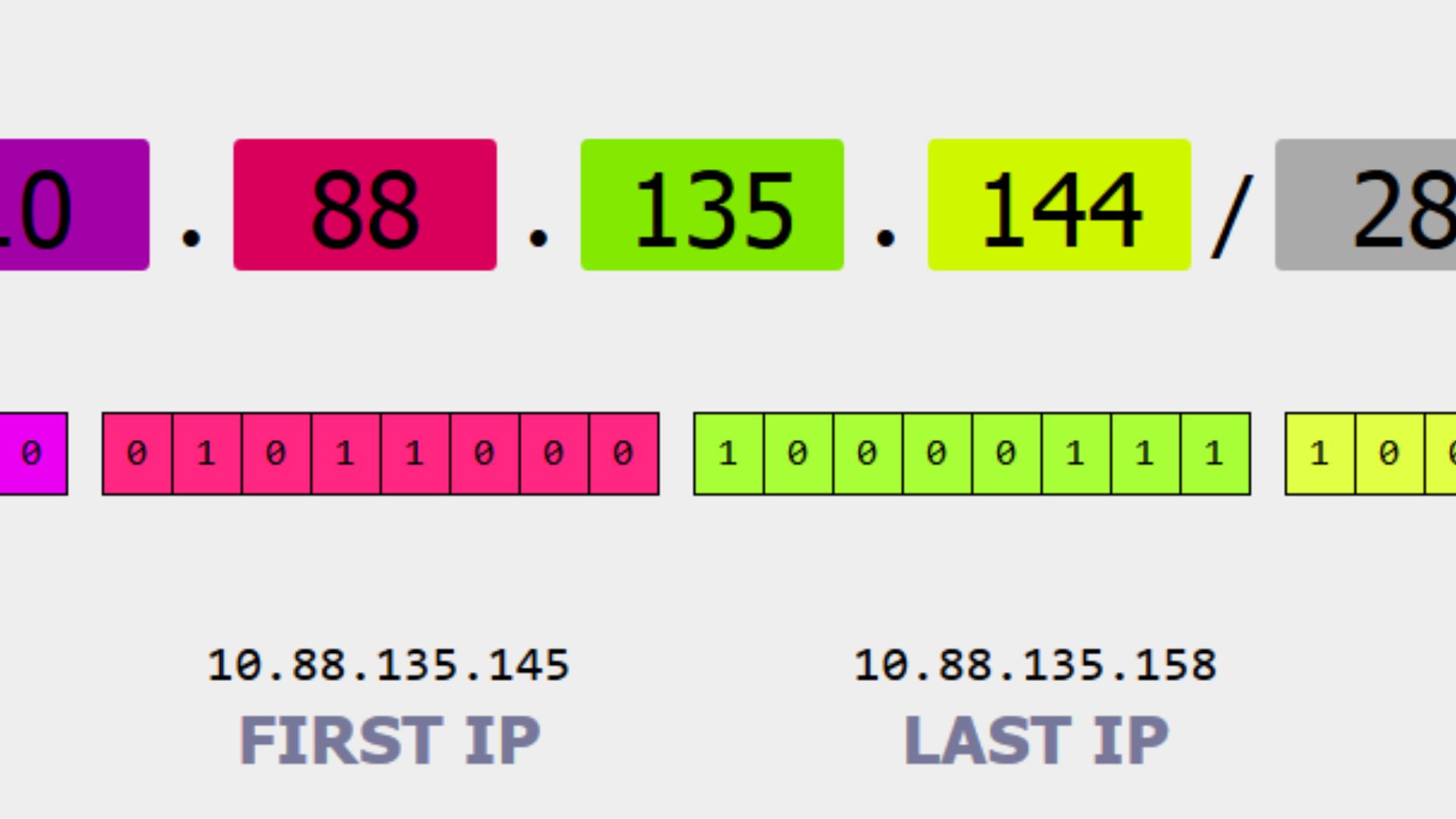
CIDR blocks are represented using a CIDR notation, which consists of an IP address followed by a forward slash and a number that specifies the number of bits in the network portion of the address. For example, the CIDR notation for a block of 256 IP addresses would be 192.168.1.0/24. This means that the first 24 bits of the IP address are used to identify the network, and the remaining 8 bits are used to identify individual devices.
CIDR XYZ takes this approach one step further by allowing network administrators to assign IP addresses based on more granular criteria. For example, instead of assigning IP addresses based on the physical location of a device, CIDR XYZ allows administrators to allocate IP addresses based on the type of device or application.
This approach enables administrators to allocate IP addresses more efficiently and to reduce the risk of IP address conflicts.
Benefits Of CIDR XYZ
CIDR XYZ offers several benefits over traditional IP address management methods, including:
Improved Efficiency
By grouping IP addresses into smaller, more manageable blocks, CIDR XYZ enables network administrators to allocate IP addresses more efficiently. This approach reduces the risk of IP address conflicts and helps to minimize IP address wastage.
Greater Control
CIDR XYZ provides network administrators with greater control over IP address allocation. This approach enables administrators to allocate IP addresses based on more granular criteria, such as the type of device or application. This approach enables administrators to optimize IP address allocation and reduce the risk of IP address conflicts.
Reduced Costs
By reducing IP address wastage and improving efficiency, CIDR XYZ can help organizations to reduce their costs associated with IP address management. This approach also enables organizations to optimize their network infrastructure and reduce the number of IP addresses required.
Scalability
CIDR XYZ is highly scalable, enabling organizations to easily expand their network infrastructure as their requirements grow. This approach also helps organizations to future-proof their network infrastructure and reduce the need for costly upgrades.
Implementation Of CIDR XYZ
Implementing CIDR XYZ requires careful planning and coordination. Network administrators must ensure that all devices and subnetworks are correctly configured to use the new IP address management approach. This process may involve updating existing network infrastructure and reconfiguring network devices.
To ensure a smooth transition to CIDR XYZ, network administrators may choose to implement the new IP address management approach gradually. This approach enables administrators to test and refine the new approach before fully implementing it across their entire network infrastructure.
CIDR XYZ And Network Security
CIDR XYZ can have a significant impact on network security by providing administrators with greater control over IP address allocation. By grouping IP addresses into smaller blocks, administrators can more easily identify and monitor network traffic, which can help to detect and prevent security threats.
One way in which CIDR XYZ can improve network security is by enabling administrators to allocate IP addresses based on the type of device or application. This approach allows administrators to restrict access to sensitive resources by assigning IP addresses only to authorized devices or applications.
CIDR XYZ can also help to prevent IP address conflicts, which can be a security risk. By reducing the number of IP addresses that are available for allocation, CIDR XYZ can make it more difficult for attackers to impersonate legitimate network devices or applications.
CIDR XYZ And IPv6 Address Management
CIDR XYZ can also be used for IPv6 address management, which is becoming increasingly important as organizations transition to IPv6. IPv6 uses a 128-bit address space, which provides significantly more IP addresses than IPv4. However, managing such a large address space can be challenging.
CIDR XYZ can help to simplify IPv6 address management by grouping IP addresses into smaller blocks. This approach enables administrators to allocate IPv6 addresses more efficiently and effectively, which can help to reduce the risk of IP address conflicts and minimize address wastage.
CIDR XYZ can also help to optimize IPv6 address allocation by enabling administrators to allocate addresses based on more granular criteria. For example, administrators can allocate addresses based on the type of device or application, which can help to optimize network performance and reduce the risk of security threats.
CIDR XYZ And Network Address Translation (NAT)
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a method of remapping one IP address space into another by modifying network address information in the IP header of packets while they are in transit across a traffic routing device. NAT is commonly used in organizations to enable multiple devices to access the internet using a single public IP address.
CIDR XYZ can play a significant role in NAT by enabling administrators to more efficiently allocate IP addresses for devices that require NAT. By grouping IP addresses into smaller blocks, administrators can allocate addresses more efficiently and reduce the risk of address conflicts.
CIDR XYZ can also enable administrators to optimize the use of NAT by allocating IP addresses based on more granular criteria. For example, administrators can allocate addresses based on the type of device or application, which can help to optimize network performance and reduce the risk of security threats.

Lec-50: Subnetting in CIDR Addressing | Classless Interdomain Routing in Hindi with Example
The Role Of Automation In CIDR XYZ Management
Automation plays a critical role in CIDR XYZ management, enabling administrators to efficiently allocate IP addresses and reduce the risk of errors. Automation can help to streamline the process of IP address allocation and management, enabling administrators to focus on other critical network tasks.
One way in which automation can be used in CIDR XYZ management is through the use of IP address management (IPAM) software. IPAM software can automate the process of IP address allocation, enabling administrators to more efficiently allocate addresses and reduce the risk of errors.
Automation can also be used to monitor network traffic and detect IP address conflicts. By automatically scanning the network for conflicts, administrators can quickly identify and resolve issues, reducing the risk of network downtime and improving network performance.
How CIDR XYZ Is Different From Other IP Address Management Approaches
CIDR XYZ is different from other IP address management approaches in several key ways. First, CIDR XYZ enables administrators to allocate IP addresses based on more granular criteria, such as the type of device or application. This approach enables administrators to optimize IP address allocation and reduce the risk of IP address conflicts.
Second, CIDR XYZ groups IP addresses into smaller blocks, which can help to reduce IP address wastage and improve network efficiency. This approach differs from traditional IP address management approaches, which often allocate IP addresses based on physical location or other less granular criteria.
Finally, CIDR XYZ can be used for both IPv4 and IPv6 address management, which is a significant advantage over other IP address management approaches that may not support both address formats.
People Also Ask
How Does CIDR XYZ Impact Network Performance?
CIDR XYZ can improve network performance by enabling more efficient IP address allocation and reducing the risk of IP address conflicts.
Can CIDR XYZ Be Used In Cloud Computing Environments?
Yes, CIDR XYZ is highly scalable, making it a good option for cloud computing environments where network infrastructure needs can change rapidly.
Does CIDR XYZ Require Any Specialized Hardware Or Software?
CIDR XYZ can be implemented using standard network hardware and software, although specialized IP address management (IPAM) software can help to automate the process of IP address allocation and management.
What Are Some Common Challenges In Implementing CIDR XYZ?
Common challenges in implementing CIDR XYZ include ensuring that all devices and subnetworks are correctly configured to use the new IP address management approach and reconfiguring network devices.
How Can CIDR XYZ Help To Reduce Costs Associated With IP Address Management?
CIDR XYZ can help to reduce costs associated with IP address management by minimizing IP address wastage, improving efficiency, and reducing the number of IP addresses required.
Conclusion
CIDR XYZ is a new approach to IP address management that simplifies the process of assigning IP addresses by grouping them into smaller, more manageable blocks. This approach provides network administrators with greater control over IP address allocation and helps to minimize IP address wastage.
As the demand for IP addresses continues to grow, CIDR XYZ represents a promising new approach to IP address management. By adopting this approach, organizations can optimize their network infrastructure and reduce the costs associated with IP address management.
Jump to
What Is CIDR XYZ?
How Does CIDR XYZ Work?
Benefits Of CIDR XYZ
Implementation Of CIDR XYZ
CIDR XYZ And Network Security
CIDR XYZ And IPv6 Address Management
CIDR XYZ And Network Address Translation (NAT)
The Role Of Automation In CIDR XYZ Management
How CIDR XYZ Is Different From Other IP Address Management Approaches
People Also Ask
Conclusion

Anderson Patterson
Author
Anderson Patterson, a tech enthusiast with a degree in Computer Science from Stanford University, has over 5 years of experience in this industry.
Anderson's articles are known for their informative style, providing insights into the latest tech trends, scientific discoveries, and entertainment news.
Anderson Patterson's hobbies include exploring Crypto, photography, hiking, and reading.
Anderson Patterson's hobbies include exploring Crypto, photography, hiking, and reading.
In the Crypto niche, Anderson actively researches and analyzes cryptocurrency trends, writes informative articles about blockchain technology, and engages with different communities to stay updated on the latest developments and opportunities.

Darren Mcpherson
Reviewer
Darren Mcpherson brings over 9 years of experience in politics, business, investing, and banking to his writing. He holds degrees in Economics from Harvard University and Political Science from Stanford University, with certifications in Financial Management.
Renowned for his insightful analyses and strategic awareness, Darren has contributed to reputable publications and served in advisory roles for influential entities.
Outside the boardroom, Darren enjoys playing chess, collecting rare books, attending technology conferences, and mentoring young professionals.
His dedication to excellence and understanding of global finance and governance make him a trusted and authoritative voice in his field.
Latest Articles
Popular Articles