Digital Wallets Decoded - Elevate Your Transactions With Dollars In The Cloud
Explore the future of finance with our comprehensive guide to digital wallets. Discover the convenience of secure transactions, seamless payments, and the latest innovations in the world of digital finance.
Author:Dexter CookeReviewer:Darren McphersonJan 08, 202436.4K Shares935.8K Views

Seamlessly integrating technology into our daily lives, digital wallets provide a secure and convenient avenue for financial interactions. This paradigm shift towards digitalization not only enhances the efficiency of transactions but also ensures the safety of sensitive information.
From contactless payments to managing diverse currencies, the versatility of digital wallets empowers users to navigate the evolving realm of financial technology. Join us on a journey into the heart of digital finance as we unravel the intricacies and possibilities that digital wallets bring to the forefront of the financial landscape.
What Is A Digital Wallet?
A digital wallet is a virtual repository that revolutionizes traditional methods of carrying and using money. Functioning as a secure, electronic version of a physical wallet, it enables users to store and manage various forms of payment information in a digital format.
At its core, a digital wallet securely stores credit/debit card details, bank account information, and, in some cases, even cryptocurrencies. The primary purpose is to facilitate seamless and convenient financial transactions, both online and offline.
The mechanics of a digital wallet involve encryption technology to safeguard sensitive data. When a user adds payment details to the wallet, the information undergoes encryption, converting it into a secure code.
This encrypted data is stored within the digital wallet, making it resistant to unauthorized access. When a user initiates a transaction, the digital wallet retrieves the necessary payment details, decrypts them for the transactional process, and then re-encrypts the information after completion.
How Does A Digital Wallet Works?
Applications called digital wallets are made to maximize the potential of mobile devices to provide better access to financial services and products. Because digital wallets store all of a user's payment information securely and compactly, they effectively do away with the necessity for traditional wallets.
Digital wallets transfer payment data securely from your mobile device to a point of sale that is set up to read the data and connect via these signals by using the wireless capabilities of your smartphone, such as Bluetooth, WiFi, and magnetic signals.
At the moment, digital wallets and mobile devices use the following technologies:
- QR codes - Quick response codes, or QR codes, are information-storing matrix bar codes. To start the payment process, you use the wallet's scanning mechanism and the camera on your device.
- Near field communication - Near field communication, or NFC, is a technology that uses electromagnetic signals to link and transfer data between two smart devices. For a connection to occur, two devices must be near one another.
- Magnetic secure transmission - The same technology that magnetic card readers use to read your card when you swipe it through a slot at a point of sale is known as magnetic secure transmission, or MST. This encrypted field, which the point of sale can read, is generated by your phone. However, Samsung, a provider of mobile phones and digital wallets, has phased out the MST technology for Samsung Pay on its Android phones.
The point-of-sale terminal, which is connected to payment processors, receives the card information that you have stored in your wallet and decide to use for a transaction. After then, the payment is sent through banks and credit card networks via processors, gateways, acquirers, or any other third parties participating in credit and debit card transactions.
Types Of Digital Wallets
Digital walletshave evolved into diverse forms, catering to various preferences and needs. Understanding the types of digital wallets is essential for users navigating the digital financial landscape. This overview explores different categories, each with its unique features and applications.
- Closed Wallet- A business that offers goods and/or services can create a closed wallet for clients. When a wallet is closed, its users can only transact with the wallet's issuer using the funds they have deposited. The wallets hold the funds from refunds, returns, and cancellations. One illustration of a closed wallet is Amazon Pay.
- Semi-closed Wallet- Users can transact at the merchants and venues listed when using a semi-closed wallet. These wallets can be used for both online and offline purchases, albeit having a limited coverage area. To accept payments from mobile wallets, however, retailers must sign contracts or agreements with the issuers.
- Open Wallet- Open wallets are provided by banks or institutions that work with banks. Users that have open wallets can utilize them for any transaction that can be done with a semi-closed wallet, including transfers and bank and ATM withdrawals.
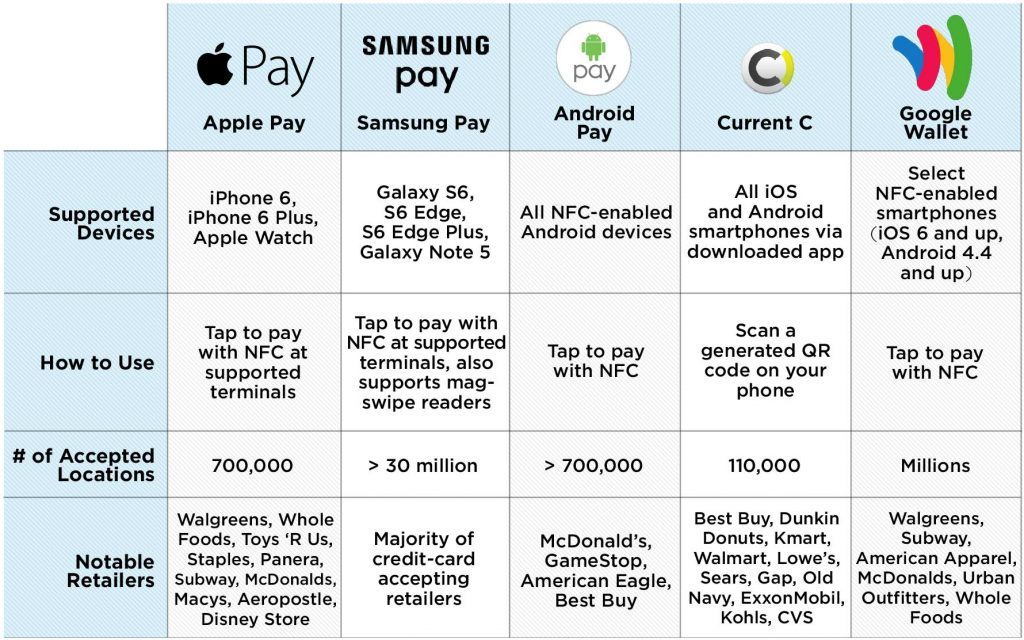
- Mobile Wallets -Mobile wallets are perhaps the most common type, residing as applications on smartphones. They store credit/debit card information, enabling users to make payments via their mobile devices. Prominent examples include Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay.
- Web Wallets -Web wallets, also known as online wallets, operate through web browsers. Users can access these wallets on any device with an internet connection, providing flexibility. PayPal and Skrill are popular examples of web wallets.
- Desktop Wallets -Desktop wallets are applications installed on a user's computer. They provide a higher level of control and security, making them ideal for users who prefer managing their finances on a desktop. Electrum and Exodus are examples of desktop wallets.
- Hardware Wallets -Hardware wallets are physical devices designed specifically for storing cryptocurrency. They offer an extra layer of security by keeping private keys offline. Ledger and Trezor are well-known hardware wallet brands.
- Contactless/NFC Wallets -Contactless or Near Field Communication (NFC) wallets enable users to make transactions by tapping their devices near a compatible terminal. These wallets are often associated with mobile payment systems like Apple Pay and Google Pay.
- Cryptocurrency Wallets -Specialized wallets designed for cryptocurrencies are known as cryptocurrency wallets. They come in various forms, including software wallets, hardware wallets, and paper wallets. Examples include Coinbase for software wallets and Ledger Nano S for hardware wallets.
Digital Wallet Examples
One Touch PayPal
The PayPal One Touch app is an addition to the standard services that PayPal provides. By removing the login screen and the requirement to input passwords, allows users to make payments or transfer money more quickly. You can use PayPal's mobile wallet app on a desktop computer, laptop, or tablet.
The Apple Pay System
The simplified Apple Pay digital software is only accessible to owners of iPhones, iPads, and Apple watches. Users can use it to transact for both in-person and online purchases. Users can unlock their phones and place them close to a suitable point-of-sale system to conduct in-store transactions. Payments may be made easily and securely with the help of the Apple Pay app.
Google Pay
With the Google Pay app, users may use their debit or credit card information to make purchases on any website or app that is linked to their Google Account, Google Play, YouTube, Android phones, and watches. Other electronic papers, including store cards, cinema tickets, gift coupons, student IDs, and transit tickets, can also be supported by the app.
Pros And Cons Of Digital Wallets
Digital wallets, heralded as a transformative force in the realm of finance, come with a set of pros and cons that users should consider.
Pros
- Convenience -Digital wallets offer unparalleled convenience, allowing users to make quick and hassle-free transactions. With just a tap or scan, payments can be executed swiftly, reducing the need for physical cards or cash.
- Enhanced Security -The encryption technology employed by digital wallets ensures that sensitive information is safeguarded. Additionally, many digital wallets incorporate biometric authentication or PIN codes, adding extra layers of security, making them less susceptible to theft or fraud compared to traditional wallets.
- Expense Tracking -Some digital wallets provide features for tracking expenses and budget management. Users can monitor their spending patterns, set limits, and receive notifications, contributing to better financial management.
- Global Accessibility -Digital wallets facilitate international transactions, offering users the ability to make purchases or transfers across borders. This feature is particularly advantageous for travelers, eliminating the need for currency exchange or carrying physical cash.
- Contactless Payments -In an era where hygiene and health are paramount, the contactless nature of digital wallets is a significant advantage. Users can make payments without physically touching surfaces, reducing the risk of germ transmission.
Cons
- Dependency on Technology -The reliance on smartphones and electronic devices is a potential drawback. Users without access to these technologies may find it challenging to adopt digital wallets, limiting financial inclusion.
- Security Concerns -While digital wallets prioritize security, the digital realm is not immune to cyber threats. Hacking attempts, phishing, or malware attacks could compromise the security of digital wallet users.
- Compatibility Issues -Not all merchants or financial institutions may accept all digital wallet platforms. This lack of universal acceptance can be inconvenient for users who may need to switch between different payment methods.
- Risk of Loss -In the event of a lost or stolen device, the risk of unauthorized access to the digital wallet exists. However, most digital wallets implement measures for remote locking or deactivating accounts to mitigate this risk.
- Limited Anonymity -Digital wallets often require user verification, reducing the level of anonymity compared to cash transactions. Some users may be concerned about the privacy implications of their financial activities being tracked.
How To Pick A Digital Wallet?
Selecting the best digital wallet is a crucial decision that hinges on various factors, each impacting the overall user experience. Here's a guide on how to pick a digital wallet tailored to individual needs.
- Security Features -Prioritize digital wallets with robust security measures. Look for encryption protocols, two-factor authentication, and biometric verification options to ensure the safety of your financial information.
- Compatibility -Consider the compatibility of the digital wallet with your devices and the operating systems they run on. Ensure the wallet aligns with your smartphone, tablet, or computer to guarantee seamless integration into your daily life.
- Accepted Payment Methods - Check which payment methods are supported by the digital wallet. Some wallets may be limited to certain credit cards, bank accounts, or cryptocurrencies. Choose a wallet that aligns with your preferred methods of payment.
- User-Friendly Interface -Opt for a digital wallet with an intuitive and user-friendly interface. A smooth and easy-to-navigate design enhances the overall user experience, making transactions more efficient.
- Transaction Fees -Review the fee structure associated with the digital wallet. While many wallets are free to use, some may charge fees for specific transactions or services. Understand the fee implications to avoid unexpected costs.
- Reputation and Reviews -Research the reputation of the digital wallet provider and read user reviews. Feedback from other users can provide valuable insights into the reliability, security, and overall performance of the wallet.
- Additional Features -Consider any additional features offered by the digital wallet, such as budgeting tools, rewards programs, or integration with other financial apps. These extra features can enhance the utility of the wallet in managing your finances.
- Customer Support -Ensure the digital wallet provider offers reliable customer support. In case of issues or queries, having accessible and responsive customer service can be instrumental in resolving concerns promptly.
By carefully evaluating these factors, users can make an informed decision when selecting a digital wallet that aligns with their preferences, lifestyle, and financial goals.
Digital Wallets - FAQs
Are Digital Wallets Safe To Use For Online Transactions?
Yes, digital wallets prioritize security through encryption and authentication measures, making them a safe option for online transactions. Always choose reputable providers and follow best security practices to enhance safety.
What Types Of Payment Methods Can Be Linked To A Digital Wallet?
Digital wallets can link to various payment methods, including credit/debit cards, bank accounts, and even cryptocurrencies. This flexibility provides users with options to suit their preferences.
Are There Fees Associated With Using Digital Wallets?
While many digital wallet services are free to use, some may charge fees for specific transactions or services. It's essential to check the terms of the provider to understand any associated costs.
Can Digital Wallets Help In Budget Management?
Yes, some digital wallets offer features for budget tracking and spending analysis. Users can monitor their expenses, set limits, and receive notifications, contributing to better financial management.
Which Digital Wallet Is Best For International Travel?
Several digital wallets cater to international travelers. Options like PayPal, Apple Pay, and Google Pay are widely accepted, allowing users to make secure transactions in various countries.
Final Words
Digital wallets stand as a testament to the ever-evolving synergy between technology and finance. As we bid farewell to traditional methods, the era of digital wallets beckons, offering unparalleled convenience and security. The continuous innovation in this space promises a future where financial transactions are not just transactions but seamless, intelligent interactions.
Embrace the digital revolution, where your wallet is no longer confined to your pocket but expands into the vast realm of possibilities. Whether you're a seasoned tech enthusiast or a curious newcomer, the world of digital wallets invites you to redefine your financial journey, one secure and efficient transaction at a time.

Dexter Cooke
Author
Dexter Cooke is an economist, marketing strategist, and orthopedic surgeon with over 20 years of experience crafting compelling narratives that resonate worldwide.
He holds a Journalism degree from Columbia University, an Economics background from Yale University, and a medical degree with a postdoctoral fellowship in orthopedic medicine from the Medical University of South Carolina.
Dexter’s insights into media, economics, and marketing shine through his prolific contributions to respected publications and advisory roles for influential organizations.
As an orthopedic surgeon specializing in minimally invasive knee replacement surgery and laparoscopic procedures, Dexter prioritizes patient care above all.
Outside his professional pursuits, Dexter enjoys collecting vintage watches, studying ancient civilizations, learning about astronomy, and participating in charity runs.

Darren Mcpherson
Reviewer
Darren Mcpherson brings over 9 years of experience in politics, business, investing, and banking to his writing. He holds degrees in Economics from Harvard University and Political Science from Stanford University, with certifications in Financial Management.
Renowned for his insightful analyses and strategic awareness, Darren has contributed to reputable publications and served in advisory roles for influential entities.
Outside the boardroom, Darren enjoys playing chess, collecting rare books, attending technology conferences, and mentoring young professionals.
His dedication to excellence and understanding of global finance and governance make him a trusted and authoritative voice in his field.
Latest Articles
Popular Articles