Eczema - Unlock The Key To Healthy And Radiant Skin
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It makes the skin red, swollen, and itchy, which can be very uncomfortable and embarrassing.
Author:Stefano MclaughlinReviewer:Dexter CookeFeb 10, 202359.9K Shares1.2M Views
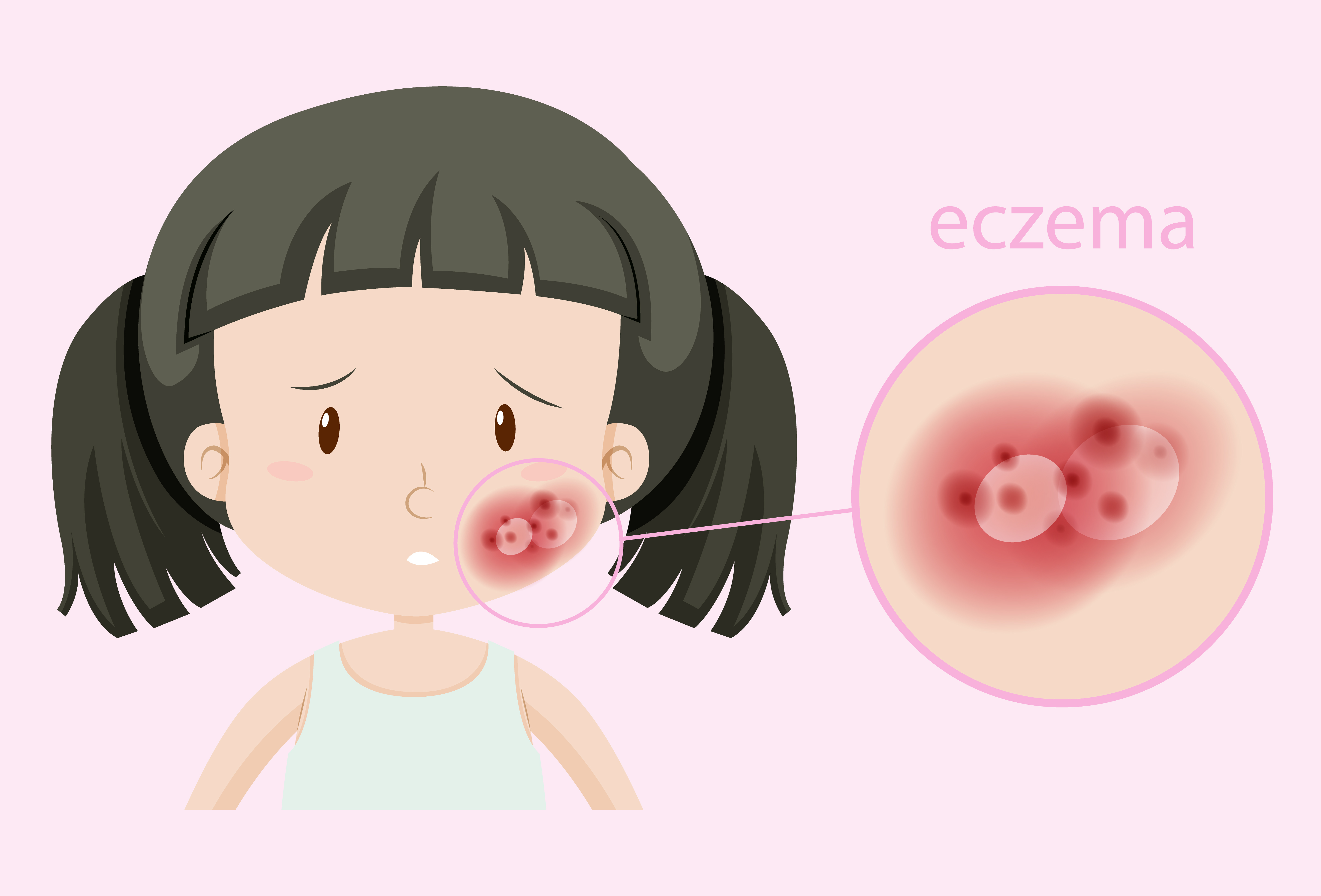
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed skin that can be extremely uncomfortable and embarrassing.
Although the exact cause of eczema is unknown, it is believed to be a combination of genetics, environmental factors, and an overactive immune system. Treatment for eczema varies depending on the severity of the condition and the individual's specific needs.
What Is Eczema?
Eczema is a non-contagious skin condition that affects people of all ages, but it is most common in children. It is characterized by dry, red, and itchy skin that can become painful and crack, leading to secondary infections. Eczema can be mild, with occasional flare-ups, or severe and persistent, affecting a person's quality of life.
There is no known cure for eczema, but with proper treatment, it can be managed and controlled. Treatment plans typically include avoiding triggers, using moisturizers, and taking medications as prescribed. Triggers for eczema can vary from person to person, but common triggers include stress, harsh soaps and detergents, certain fabrics, and environmental allergens.
It is important for those with eczema to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan that works best for them. With the right combination of treatments and lifestyle changes, it is possible to achieve clearer, healthier skin and reduce the frequency and severity of eczema symptoms.
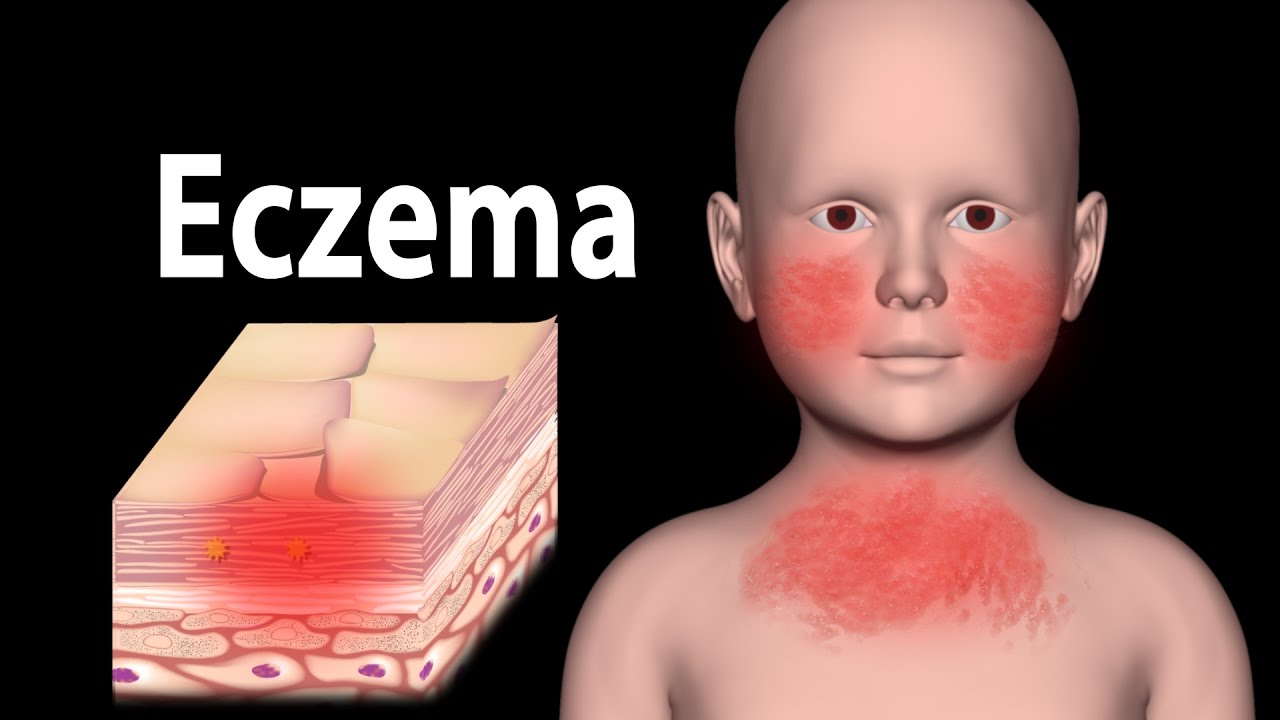
Eczema, Animation.
What Causes Eczema?
Multiple factors contribute to the development of eczema, making it difficult to pinpoint a single factor as the cause. We think that both environmental and genetic factors contribute to eczema. Certain environmental variables might also induce eczema. These elements include:
- Allergens:Allergens are the primary cause of allergic eczema. These allergens include pollens, dust particles, dogs, etc.
- Irritants include specific soaps, shampoos, washing powder, and food items such as fruit juice, vegetables, and meats, among others. Irritants are substances that induce allergic responses in the human body.
- Certain kinds of bacteria, viruses, and fungus fall within this classification.
- Intolerant foods:If you are intolerant to certain foods, you may get eczema. This category include items such as nuts & seeds, dairy products, and eggs.
- Temperature change:In a few instances, dramatic weather changes and, above all, intense perspiration may lead to severe eczema.
- Female patients are more likely to acquire eczema during pregnancy or during a specific phase of the menstrual cycle due to hormones. It might arise as a result of fluctuating hormone levels in their body.
- Even while stress does not directly cause eczema, it may exacerbate the symptoms.
Prevention And Management Of Eczema
Prevention and management of eczema involves a combination of avoiding triggers, using moisturizers, and following a balanced and healthy diet. Here are some tips for preventing and managing eczema:
- Avoid triggers: Triggers for eczema can vary from person to person, but common triggers include stress, harsh soaps and detergents, certain fabrics, and environmental allergens. Avoiding triggers can help reduce the frequency and severity of eczema symptoms.
- Use moisturizers regularly:Keeping the skin moisturized is crucial in preventing and managing eczema. Use fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizers several times a day to keep the skin hydrated.
- Follow a balanced and healthy diet:A balanced and healthy diet can help support overall skin health and prevent eczema flare-ups. Eating a diet rich in essential fatty acids, vitamins, and antioxidants can help maintain skin health.
- Keep stress levels low:Stress can be a trigger for eczema and can worsen symptoms. It is important to find ways to manage stress levels, such as through exercise, relaxation techniques, or therapy.
- Avoid scratching:Scratching can make eczema symptoms worse and lead to secondary infections. Keeping the skin moisturized, using topical creams and ointments, and using cool compresses can help reduce the urge to scratch.
Working closely with a healthcare provider can help develop an individualized prevention and management plan for eczema. With the right combination of treatments and lifestyle changes, it is possible to achieve clearer, healthier skin and reduce the frequency and severity of eczema symptoms.
Treatment For Eczema
Treatment for eczema varies depending on the severity of the condition and the individual's specific needs. Here are some common treatments for eczema:
- Over-the-counter creams and ointments: Over-the-counter creams and ointments, such as hydrocortisone, can help relieve itching and inflammation.
- Prescription medications:In more severe cases of eczema, prescription medications, such as topical calcineurin inhibitors and topical corticosteroids, may be prescribed to manage symptoms.
- Phototherapy:Phototherapy, also known as light therapy, uses ultraviolet light to reduce inflammation and improve the appearance of the skin.
- Natural remedies:Some individuals with eczema may choose to use natural remedies, such as aloe vera, coconut oil, or chamomile, to manage symptoms. It is important to discuss these options with a healthcare provider before trying them.
- Alternative therapies:Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture and herbal remedies, may be used to manage eczema symptoms in some individuals. Again, it is important to discuss these options with a healthcare provider before trying them.
Living With Eczema
Living with eczema can be challenging, but with the right combination of treatments and lifestyle changes, it is possible to achieve clearer, healthier skin and reduce the frequency and severity of symptoms. Working closely with a healthcare provider is crucial in developing an individualized treatment plan that works best for you.
A balanced and healthy diet can help support overall skin health and prevent eczema flare-ups. Eating a diet rich in essential fatty acids, vitamins, and antioxidants can help maintain skin health.
People Also Ask
Can Eczema Be Cured?
Currently, there is no cure for eczema, but it can be managed and controlled with proper treatment.
Is Eczema Contagious?
No, eczema is not contagious and cannot be spread from person to person.
Can Stress Cause Eczema?
Stress can exacerbate eczema symptoms and make the condition worse.
Final Thought
Eczema is a frustrating and uncomfortable skin condition that can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life. However, with the right treatment plan and lifestyle changes, it is possible to manage eczema and achieve clearer, healthier skin.
Whether it be through over-the-counter creams and ointments, prescription medications, or natural remedies, there is hope for those who suffer from eczema.
It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan and find the right solution for you.

Stefano Mclaughlin
Author
Stefano Mclaughlin is a Psychologist focused on mental health, emotional well-being, and healthcare policy. He studied Psychology and Public Health at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, gaining a deep understanding of the intersection between mental health and public policy.
Stefano's mission is clear: he aims to destigmatize mental health discussions, improve access to mental healthcare, and promote emotional well-being for all. Drawing from personal experiences with anxiety and depression, Stefano shares real stories to make mental health topics more relatable and less intimidating.
In addition to his advocacy work, Stefano enjoys delving into books, experimenting in the kitchen, and embarking on new adventures. These hobbies fuel his creativity and inspire fresh perspectives for his advocacy work.

Dexter Cooke
Reviewer
Dexter Cooke is an economist, marketing strategist, and orthopedic surgeon with over 20 years of experience crafting compelling narratives that resonate worldwide.
He holds a Journalism degree from Columbia University, an Economics background from Yale University, and a medical degree with a postdoctoral fellowship in orthopedic medicine from the Medical University of South Carolina.
Dexter’s insights into media, economics, and marketing shine through his prolific contributions to respected publications and advisory roles for influential organizations.
As an orthopedic surgeon specializing in minimally invasive knee replacement surgery and laparoscopic procedures, Dexter prioritizes patient care above all.
Outside his professional pursuits, Dexter enjoys collecting vintage watches, studying ancient civilizations, learning about astronomy, and participating in charity runs.
Latest Articles
Popular Articles