How Long Does Thermal Paste Last? Everything You Need To Know
How long does thermal paste last? This guide covers everything you need to know, from choosing the right thermal paste to applying it correctly to extending its lifespan.
Author:Anderson PattersonReviewer:Darren McphersonDec 23, 20231.9K Shares136.1K Views

Thermal paste is a vital component of computer assembly and maintenance, serving as a heat-conductive interface between the CPU and the heatsink. Its lifespan is crucial for optimal performance and durability of computing devices. In this blog post, we explore the intricacies of thermal paste, including how long does thermal paste last, its application, and lifespan determinants. Understanding the longevity of thermal paste is essential for IT professionals and everyday users alike, as it plays a pivotal role in maintaining the efficiency and stability of a computer's cooling system.
This comprehensive guide demystifies this often-overlooked yet essential aspect of computer maintenance. We investigate how environmental conditions, paste quality, and computer usage intensity impact thermal paste performance and degradation. Additionally, we provide practical insights on identifying the signs of thermal paste degradation and the recommended reapplication intervals.
Whether you are building a new PC, upgrading an existing system, or simply seeking to improve your computer's performance, this article provides all you need to know about thermal paste lifespan and maintenance.
What Is Thermal Paste?
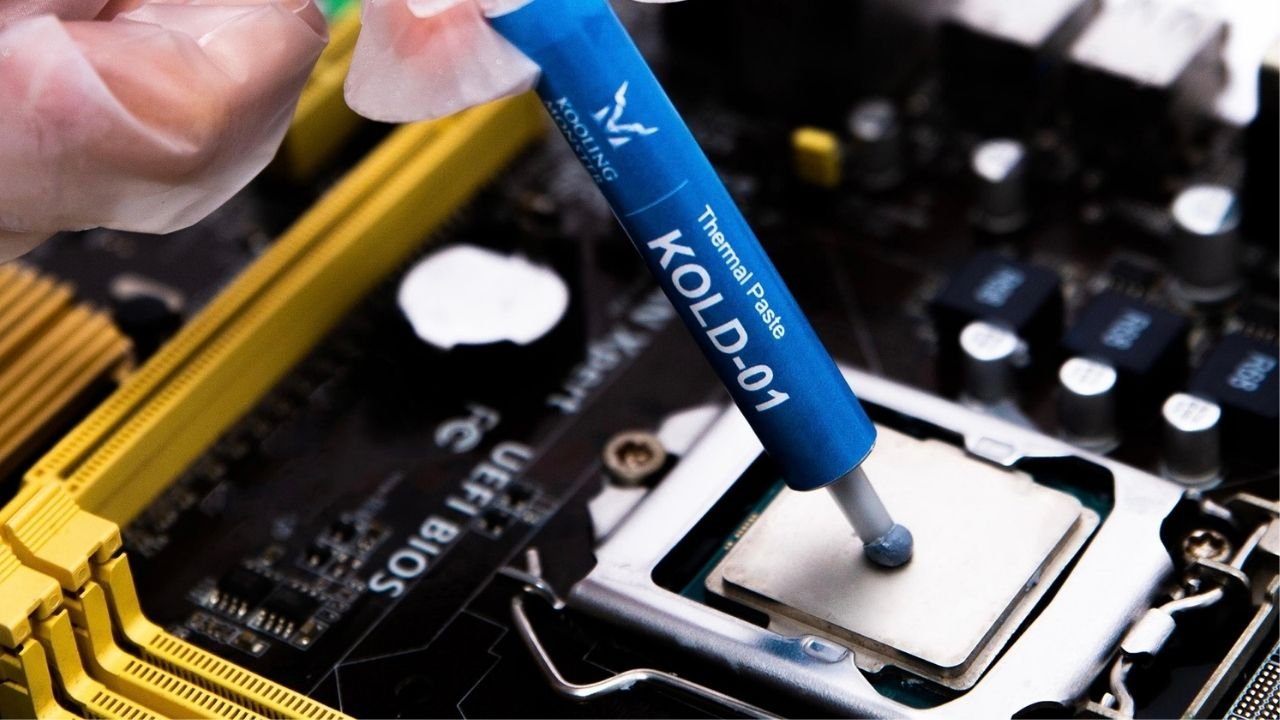
Thermal paste, also known as thermal compound, thermal interface material (TIM), thermal gel, or heat paste, is a thermally conductive (but usually electrically insulating) compound that is commonly used as an interface between heat sinks and heat sources such as high-power semiconductor devices. The main role of thermal paste is to eliminate air gaps or spaces (which act as thermal insulation) from the interface area in order to maximize heat transfer and dissipation.
What Is Thermal Paste Made Of?
Thermal paste is typically composed of a mixture of metal oxides and silicone oil. The metal oxides provide thermal conductivity, while the silicone oil helps to keep the paste moist and pliable. Thermal pastes can also contain other additives, such as carbon nanotubes or ceramic particles, to further improve their thermal conductivity.
How Does Thermal Paste Work?
When thermal paste is applied between a heat sink and a heat source, it fills in any microscopic air gaps or spaces that may be present. This allows for more efficient heat transfer from the heat source to the heat sink. Thermal paste is also typically more viscous than air, which helps to prevent convection currents from forming. This further improves heat transfer efficiency.
Role Of Thermal Paste In Computer Performance
Thermal paste plays a vital role in the performance and durability of computers. By helping to keep the CPU cool, thermal paste prevents throttling, which is a process where the CPU reduces its performance to avoid overheating. Thermal paste also helps to extend the lifespan of the CPU by preventing it from being damaged by excessive heat.
Do Thermal Pastes Expire?
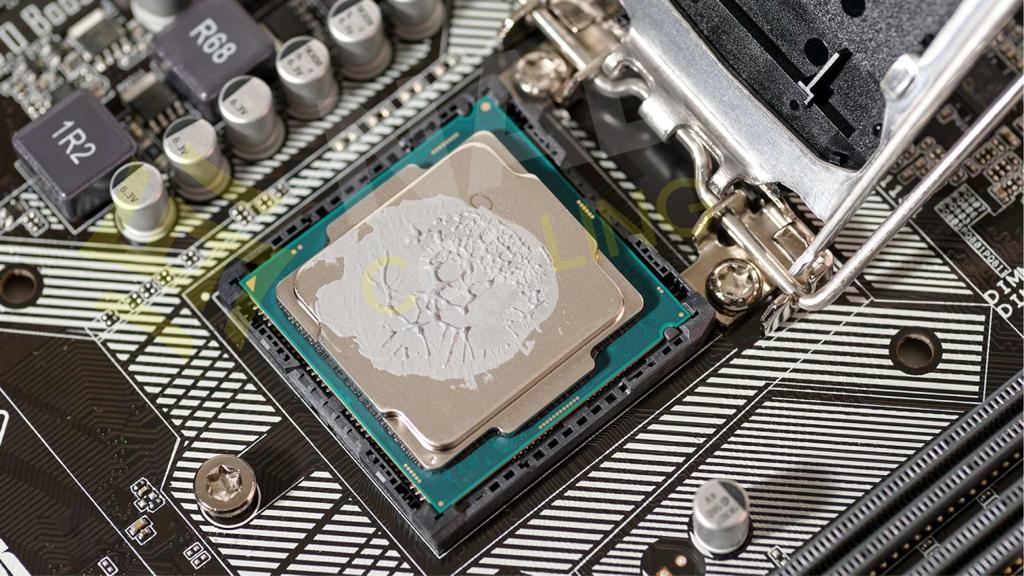

Shelf Life And Expiration Of Unopened Thermal Paste
Yes, thermal pastes do expire. The shelf life of unopened thermal paste varies depending on the brand and formula, but it typically ranges from 2 to 3 years. After this period, the thermal paste may begin to degrade, resulting in decreased thermal conductivity and an increased risk of overheating.
There are a few factors that can affect the shelf life of thermal paste, including:
- Temperature -Extreme heat and cold can shorten the shelf life of thermal paste. It is best to store thermal paste in a cool, dry place.
- Humidity -High humidity can also shorten the shelf life of thermal paste. Avoid storing thermal paste in humid environments.
- Exposure to air -Once the thermal paste is exposed to air, it can begin to oxidize and degrade. It is important to keep the tube of thermal paste tightly capped when not in use.
Degradation Of Thermal Paste Over Time In Use
Thermal paste also degrades over time. This is due to a number of factors, including:
- Heat -The heat generated by the CPU causes the thermal paste to break down over time.
- Stress -The stress of repeated thermal cycling (heating and cooling) can also cause the thermal paste to degrade.
- Time -Even if the CPU is not in use, the thermal paste will eventually degrade over time.
The rate at which thermal paste degrades depends on a number of factors, including the quality of the paste, the operating temperature of the CPU, and the amount of stress the CPU is under. In general, high-quality thermal pastes will last longer than lower-quality pastes. Additionally, CPUs that operate at high temperatures and are under heavy stress will degrade thermal paste more quickly.
How To Tell When Thermal Paste Needs To Be Replaced
There are a few signs that the thermal paste needs to be replaced.
- Higher CPU temperatures -If you notice that your CPU temperatures are higher than usual, it may be a sign that the thermal paste needs to be replaced.
- CPU throttling -If your CPU is throttling (reducing its performance to prevent overheating), it may also be a sign that the thermal paste needs to be replaced.
- Computer crashes or restarts unexpectedly -If your computer crashes or restarts unexpectedly, it may also be a sign that the thermal paste needs to be replaced.
Does Thermal Paste Go Bad?
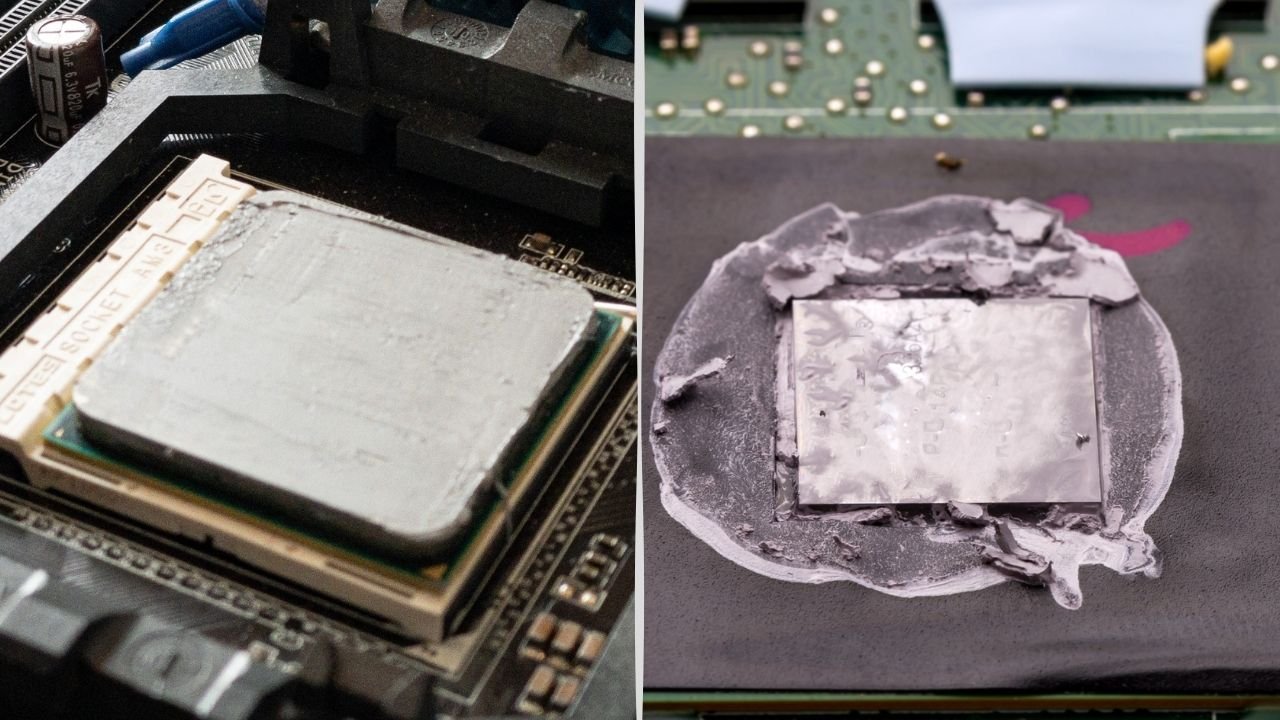
Yes, the thermal paste can go bad. Thermal paste is a suspension of heterogeneous compounds held together by a liquid. Over time, the liquid can evaporate, causing the thermal paste to dry out and become less effective at transferring heat. This can lead to higher CPU temperatures, reduced performance, and even system instability.
Do Thermal Paste Expire
There are a few signs that your thermal paste may have expired:
- Increased CPU temperatures -If you notice that your CPU temperatures are higher than usual, this could be a sign that your thermal paste has expired.
- CPU throttling -CPU throttling is a process by which the CPU reduces its performance in order to prevent overheating. If your CPU is throttling, this could be a sign that your thermal paste is not transferring heat effectively.
- Computer crashes or restarts unexpectedly -If your computer is crashing or restarting unexpectedly, this could also be a sign that your thermal paste has expired and is not transferring heat effectively.
Recognizing The Need For Replacement
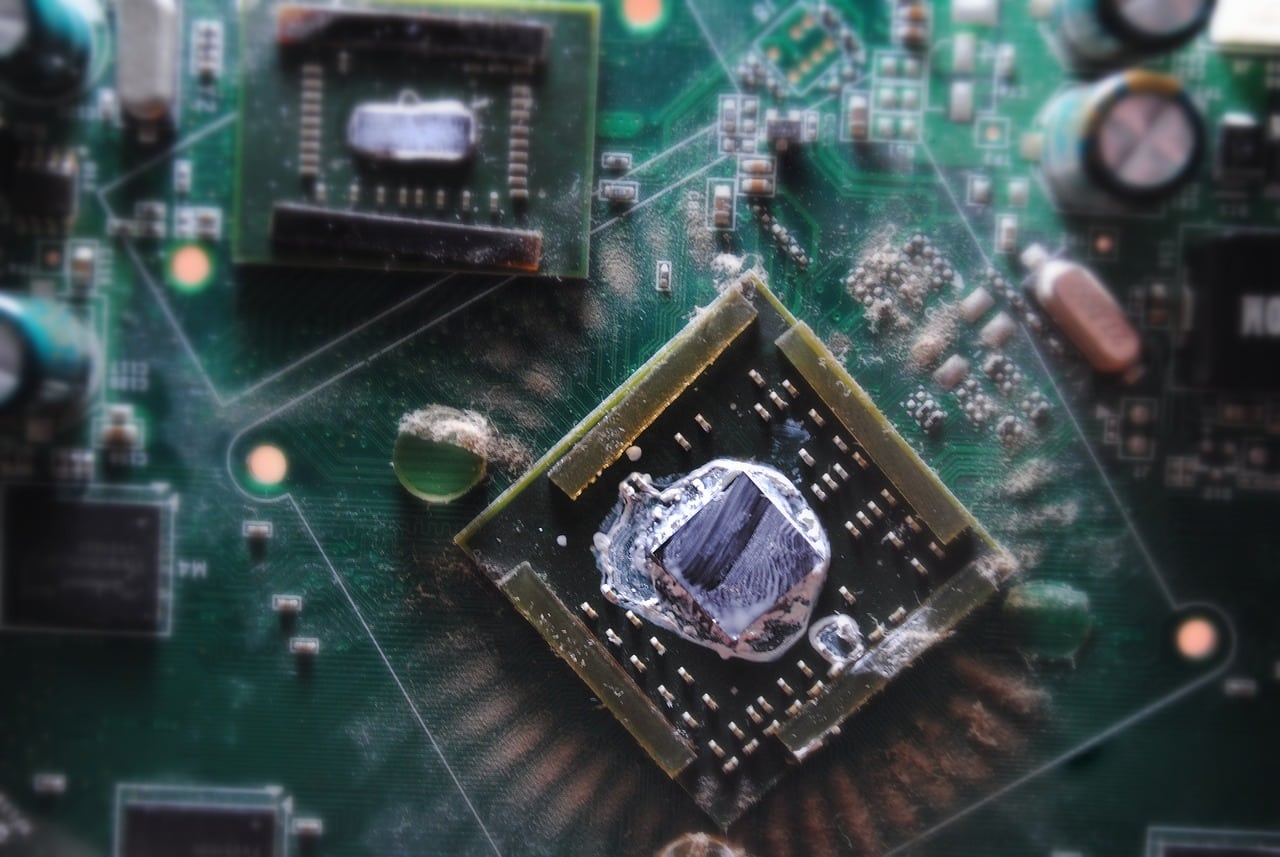
Thermal paste is a critical component of any high-performance computer system, helping to transfer heat away from the CPU and keep it cool. Over time, however, thermal paste can degrade and become less effective, leading to higher CPU temperatures and reduced performance. In some cases, it may even cause the CPU to overheat and shut down.
There are a few key signs that indicate that it may be time to replace your thermal paste:
- Higher CPU temperatures -If you notice that your CPU temperatures are running higher than usual, this could be a sign that your thermal paste is no longer performing as well as it should. You can check your CPU temperatures using a variety of software tools, such as HWMonitor or Core Temp.
- Reduced CPU performance -If you're experiencing reduced CPU performance, such as slower boot times or longer loading times for applications, this could also be a sign of thermal paste degradation.
- System instability -If your computer is crashing or restarting unexpectedly, this could be caused by a variety of factors, but thermal paste degradation can be a contributing factor.
- Computer age -Most thermal pastes have a lifespan of 2-4 years, so if your computer is older than this, it's a good idea to replace the thermal paste as a preventative measure.
Symptoms Of Thermal Paste Deterioration
There are a few physical signs that your thermal paste may be degrading, such as:
- Discoloration -Thermal paste typically has a silvery-gray color, but over time it can become discolored or even turn brown. This can be a sign that the thermal paste is no longer effective at transferring heat.
- Dryness -Thermal paste should be slightly moist, but if it becomes dry and brittle, this can also indicate that it is no longer effective.
- Cracking -If you notice any cracks in your thermal paste, this is a sure sign that it needs to be replaced.
The Impact Of Aging On Thermal Paste Efficiency
Thermal paste degrades over time due to a number of factors, including:
- Heat -Thermal paste is constantly exposed to heat from the CPU, which can cause it to break down over time.
- Airflow -If your computer has poor airflow, this can also accelerate the degradation of thermal paste.
- Dust and dirt -Dust and dirt can accumulate on thermal paste, reducing its effectiveness at transferring heat.
The rate at which thermal paste degrades will vary depending on a number of factors, including the quality of the thermal paste, the operating temperature of the CPU, and the amount of stress the CPU is under. However, even the best thermal pastes will eventually need to be replaced.
Application And Maintenance Guidelines
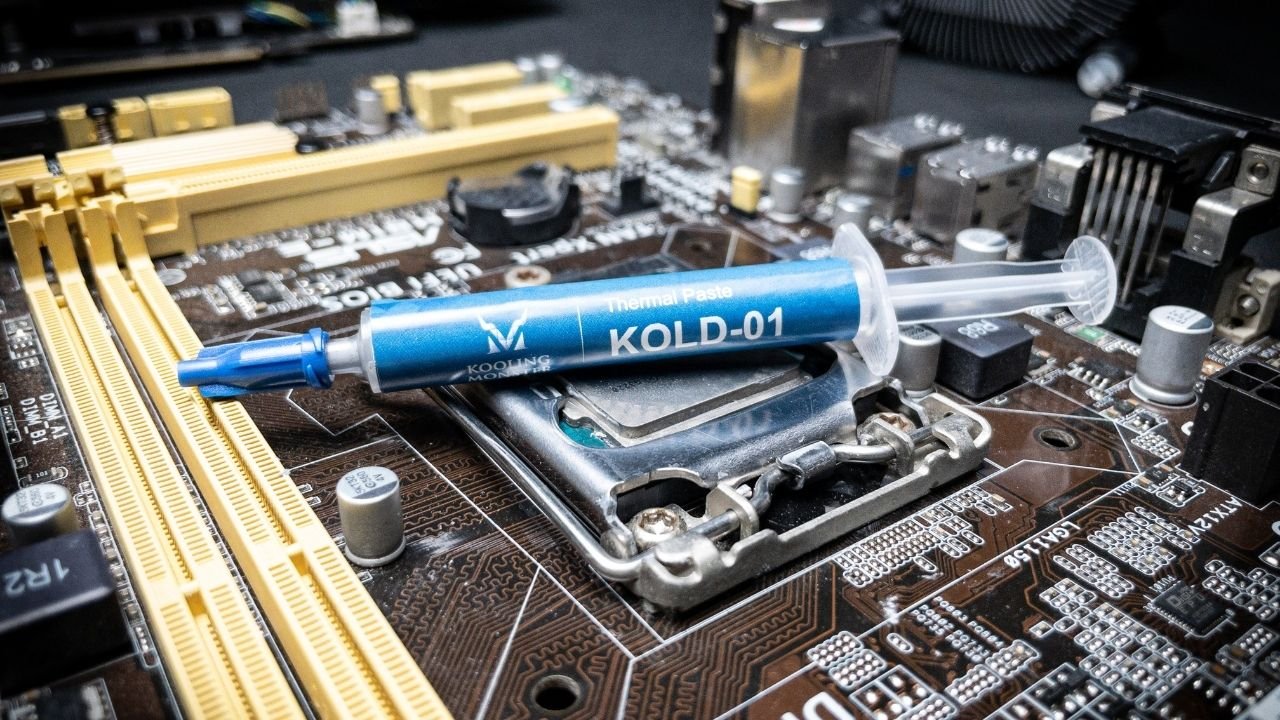

Proper Application Techniques
When applying thermal paste, it is important to follow proper application techniques to ensure that the paste is evenly distributed and that there is no excess paste. Here are some tips:
- Clean the CPU and heatsink surfaces with isopropyl alcohol to remove any dirt, dust, or old thermal paste.
- Apply a small amount of thermal paste to the center of the CPU's IHS (Integrated Heat Spreader).
- Use a thermal spreader to spread the paste evenly over the entire surface of the IHS. Be careful not to apply too much paste, as this can actually reduce heat transfer.
- Install the heatsink and tighten the mounting screws. Be sure to follow the instructions that came with your CPU cooler.
Maintenance And Reapplication Schedules
Thermal paste will eventually degrade over time, so it is important to reapply it periodically. The frequency at which you need to reapply thermal paste depends on a number of factors, including the quality of the paste, the operating temperature of the CPU, and the amount of stress the CPU is under. In general, most thermal pastes will last for about 2 to 4 years. However, some high-quality thermal pastes can last for up to 7 years.
If you are experiencing any of the following problems, it is a good idea to check your thermal paste and replace it if necessary.
- Your CPU temperatures are higher than usual.
- Your CPU is throttling (reducing its performance to prevent overheating).
- Your computer is crashing or restarting unexpectedly.
To reapply thermal paste, simply follow the application techniques described above.
Selecting The Right Thermal Paste
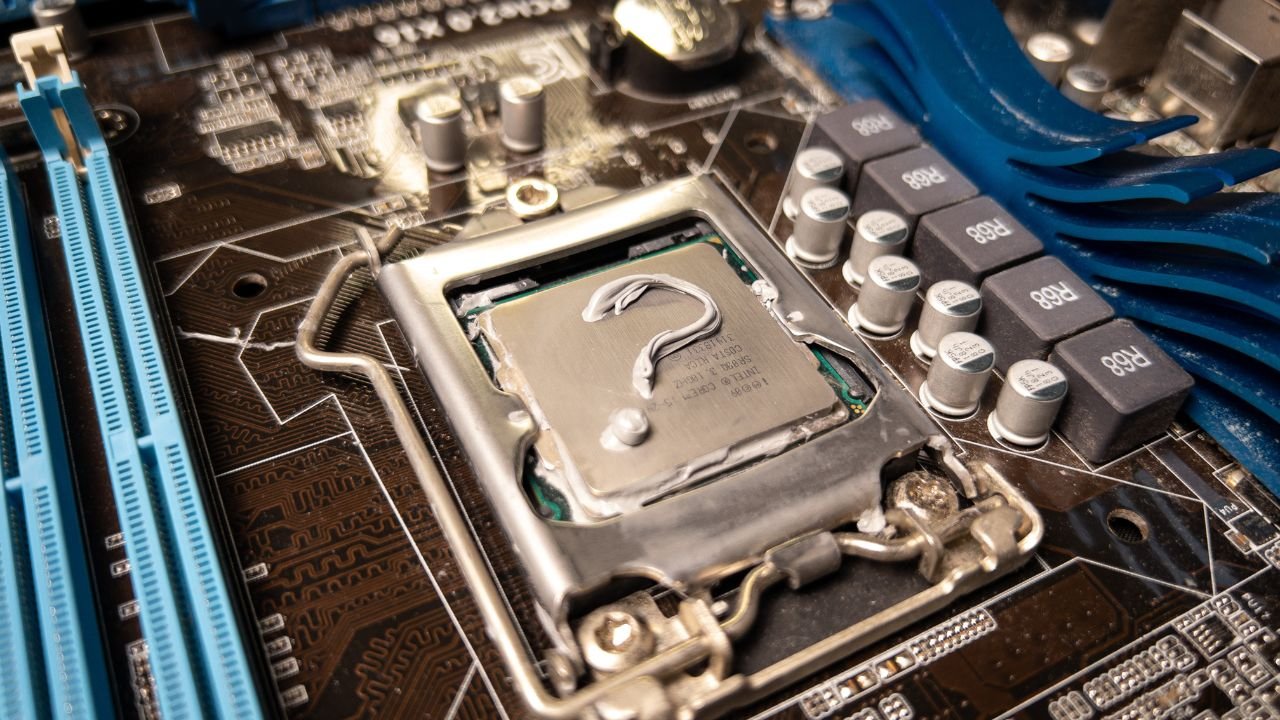

Thermal paste is a critical component of computer assembly and maintenance, serving as a heat-conductive interface between the CPU and the heatsink. It plays a vital role in maintaining optimal CPU temperatures and preventing overheating, which can lead to performance throttling, instability, and even system failure.
When selecting a thermal paste, there are a number of factors to consider, including the type of thermal paste, its thermal conductivity, viscosity, and durability.
Types Of Thermal Paste Available
There are three main types of thermal paste available:
- Silicone-based thermal paste -Silicone-based thermal paste is the most common and affordable type of thermal paste. It is easy to apply and has a good thermal conductivity. However, silicone-based thermal paste can dry out over time, necessitating more frequent reapplication.
- Metal-based thermal paste -Metal-based thermal paste has a higher thermal conductivity than silicone-based thermal paste, making it ideal for high-performance systems. However, metal-based thermal paste can be more difficult to apply and can be electrically conductive, which means it is important to be careful not to overapply it or apply it to any electrical components.
- Carbon-based thermal paste -Carbon-based thermal paste has the highest thermal conductivity of all three types of thermal paste. It is also very durable and does not dry out over time. However, carbon-based thermal paste is also the most expensive type of thermal paste and can be more difficult to find.
Matching Thermal Paste To Your Hardware Requirements
When matching thermal paste to your hardware requirements, it is important to consider the following factors:
- CPU type -The type of CPU you have will determine the amount of heat it generates. High-end CPUs will generate more heat than lower-end CPUs, so they will require a thermal paste with a higher thermal conductivity.
- CPU cooler -The type of CPU cooler you have will also affect the amount of heat that needs to be transferred from the CPU. A high-end CPU cooler will be more efficient at transferring heat than a lower-end CPU cooler, so it may be possible to use a thermal paste with a lower thermal conductivity.
- Overclocking -If you are overclocking your CPU, you will need to use a thermal paste with a higher thermal conductivity to account for the increased heat generation.
Environmental Influences On Thermal Paste
Temperature And Humidity Effects
Temperature and humidity are two of the most important environmental factors that can affect the lifespan and performance of thermal paste. Thermal paste is designed to operate within a specific temperature range, typically between 50 and 150 degrees Celsius. If the temperature of the CPU exceeds the recommended range, the thermal paste can start to degrade and lose its effectiveness. This can lead to higher CPU temperatures, reduced performance, and even system instability.
Humidity can also have a negative impact on thermal paste. If the humidity is too high, it can cause the thermal paste to absorb moisture. This can make the thermal paste less effective at transferring heat, and it can also increase the risk of corrosion.
External Factors And Their Impact
In addition to temperature and humidity, there are a number of other external factors that can affect thermal paste. These include:
- Dust and dirt -Dust and dirt can build up on the CPU and heatsink over time, which can reduce the effectiveness of the thermal paste.
- Airflow -Poor airflow in the computer case can also lead to higher CPU temperatures and reduced thermal paste performance.
- Overclocking -Overclocking the CPU can increase its temperature and put more stress on the thermal paste.
How To Minimize The Impact Of Environmental Factors On Thermal Paste
There are a few things you can do to minimize the impact of environmental factors on thermal paste:
- Keep your computer in a cool, dry environment -Avoid placing your computer near heat sources or in direct sunlight.
- Clean your computer regularly -Use a can of compressed air to remove dust and dirt from the CPU and heatsink.
- Make sure your computer has good airflow -Install additional fans if necessary.
Best Practices For Thermal Paste Usage

Summarizing Key Takeaways
- Thermal paste is a critical component of computer assembly and maintenance, serving as a heat-conductive interface between the CPU and the heatsink.
- Its lifespan is crucial for optimal performance and durability of computing devices.
- Environmental conditions, paste quality, and computer usage intensity impact thermal paste performance and degradation.
- Recognizing the signs of thermal paste degradation and reapplying thermal paste at the appropriate intervals are essential for maintaining the efficiency and stability of a computer's cooling system.
Recommendations For Optimal Thermal Paste Usage
- Thermal conductivity -The thermal conductivity of a thermal paste is a measure of how well it transfers heat. Higher thermal conductivity means better heat transfer.
- Viscosity -The viscosity of a thermal paste is a measure of how thick it is. A less viscous thermal paste will be easier to apply, but it may also be more likely to drip or run off.
- Durability -Some thermal pastes are more durable than others and can withstand higher temperatures and more stress. If you have a high-performance CPU or overclock your CPU, you may want to choose a more durable thermal paste.
- Monitor thermal paste performance -It is important to monitor thermal paste performance over time to ensure that it is still effective at transferring heat. Signs of thermal paste degradation include.
- Reapply thermal paste at the appropriate intervals -The frequency at which you need to reapply thermal paste depends on a number of factors, including the type of thermal paste you are using, the environmental conditions, and the intensity of computer usage. In general, it is a good idea to reapply thermal paste every 2-4 years, or sooner if you are experiencing any of the signs of thermal paste degradation.
Additional Tips For Optimal Thermal Paste Usage
- Avoid using too much thermal paste. Too much thermal paste can actually reduce heat transfer.
- Be careful not to get thermal paste on the pins of the CPU or the socket of the motherboard.
- If you are using a pre-applied thermal paste on your CPU cooler, clean the surface of the IHS with isopropyl alcohol before installing the cooler.
- If you are overclocking your CPU, you may want to consider reapplying thermal paste more frequently.
By following these best practices for thermal paste usage, you can help to ensure that your CPU stays cool and performs optimally for years to come.
Frequently Ask Questions - How Long Does Thermal Paste Last
How Do You Know If The Thermal Paste Is Worn Out?
If you see thermal paste watery, hard, or flaky, know that thermal paste has gone bad, so throw it away immediately. If the thermal paste has dried up in the CPU, you need to replace the thermal paste. Remove it with an isopropyl alcohol pad and put on a new layer of thermal paste.
Does Thermal Paste Ever Expire?
Do Thermal Compounds have an expiration date? Depends on the contents of the thermal compound but most should have a shelf life of around 2 years if the cap was placed on properly and it was stored in a cool location out of the sunlight.
How Often Should Thermal Paste Be Replaced?
How Often Should You Replace Thermal Paste? In most cases, you shouldn't need to reapply more than once every few years, though you should replace your paste if you remove your cooler for any reason. You may also want to consider reapplying thermal paste if you find your CPU temperatures are climbing.
Conclusion
To conclude, the lifespan of thermal paste is essential for maintaining optimal computer performance and longevity. As discussed, various factors, including the paste's composition, computer usage intensity, and environmental conditions, significantly impact its durability. Regular monitoring and timely reapplication are crucial to preventing overheating and ensuring the longevity of your computer's components. This guide aims to provide you with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions about thermal paste maintenance, ultimately enhancing your computing experience.
Jump to
What Is Thermal Paste?
Do Thermal Pastes Expire?
Does Thermal Paste Go Bad?
Recognizing The Need For Replacement
Application And Maintenance Guidelines
Selecting The Right Thermal Paste
Environmental Influences On Thermal Paste
Best Practices For Thermal Paste Usage
Frequently Ask Questions - How Long Does Thermal Paste Last
Conclusion

Anderson Patterson
Author
Anderson Patterson, a tech enthusiast with a degree in Computer Science from Stanford University, has over 5 years of experience in this industry.
Anderson's articles are known for their informative style, providing insights into the latest tech trends, scientific discoveries, and entertainment news.
Anderson Patterson's hobbies include exploring Crypto, photography, hiking, and reading.
Anderson Patterson's hobbies include exploring Crypto, photography, hiking, and reading.
In the Crypto niche, Anderson actively researches and analyzes cryptocurrency trends, writes informative articles about blockchain technology, and engages with different communities to stay updated on the latest developments and opportunities.

Darren Mcpherson
Reviewer
Darren Mcpherson brings over 9 years of experience in politics, business, investing, and banking to his writing. He holds degrees in Economics from Harvard University and Political Science from Stanford University, with certifications in Financial Management.
Renowned for his insightful analyses and strategic awareness, Darren has contributed to reputable publications and served in advisory roles for influential entities.
Outside the boardroom, Darren enjoys playing chess, collecting rare books, attending technology conferences, and mentoring young professionals.
His dedication to excellence and understanding of global finance and governance make him a trusted and authoritative voice in his field.
Latest Articles
Popular Articles