Piles - Understanding The Causes And Symptoms
Piles, also known as hemorrhoids, are a common medical condition affecting the anus and rectum. They happen when the veins in these places get swollen and inflamed, which can cause pain, itching, and even bleeding in the rectal area. There are two types of piles: internal and external, and they can range from mild to severe.
Author:Stefano MclaughlinReviewer:Dexter CookeFeb 08, 2023105.8K Shares1.6M Views
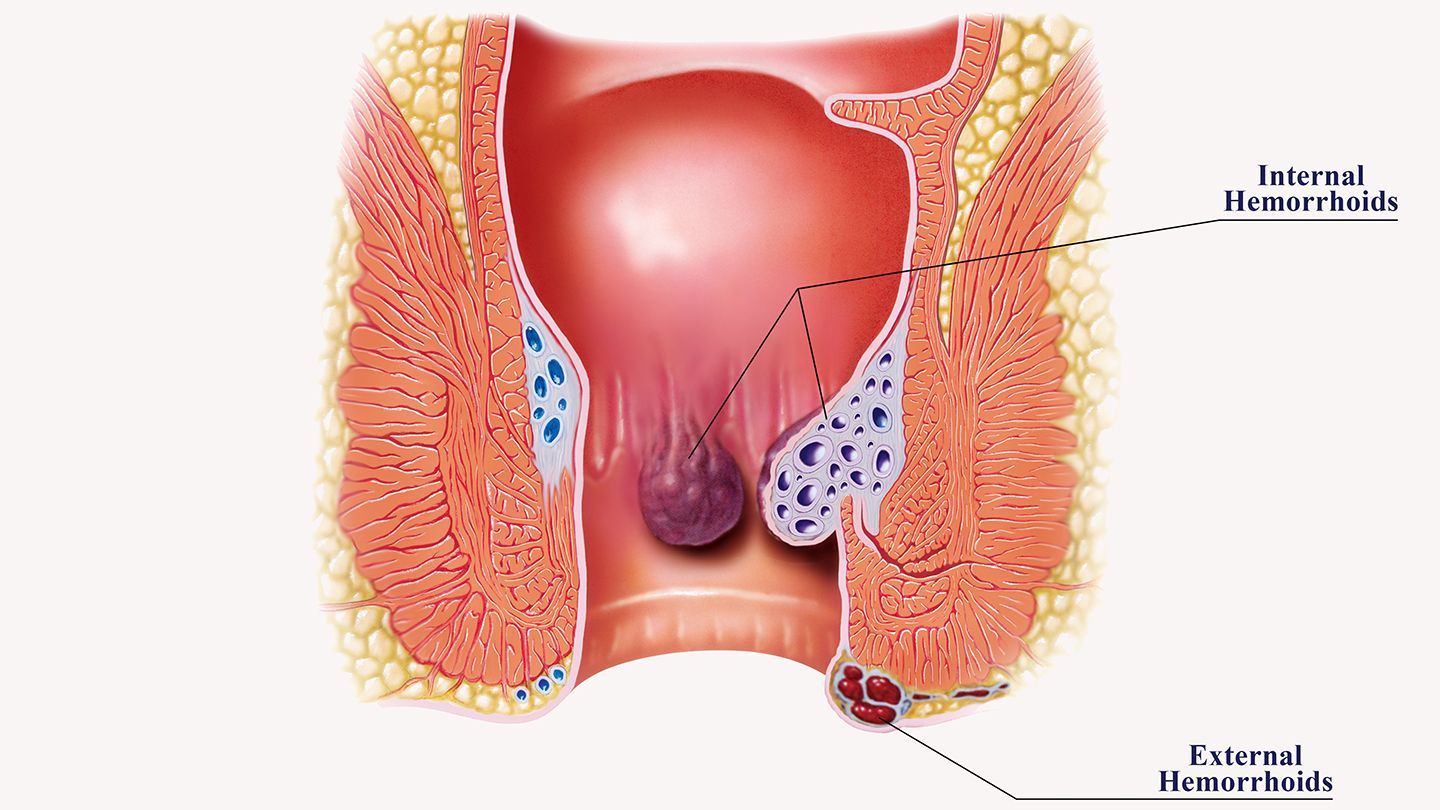
Piles, also known as hemorrhoids, are a common medical condition affecting the anus and rectum. They occur when the veins in these areas become swollen and inflamed, causing discomfort, itching, and even rectal bleeding. There are two types of piles: internal and external, and they can range from mild to severe.
What Is Piles?
Hemorrhoids, or piles, are enlargements of the veins in the anus and lower rectum. Rectal bleeding, itching, and pain are all symptoms of this frequent illness. Internal and exterior piles may vary in severity, yet both exist.
Factors including sitting for extended periods of time, being pregnant, or experiencing straining when passing feces may all contribute to the development of piles.
Over-the-counter treatments, dietary adjustments, and re-establishing healthy bowel routines are common methods of self-care for these conditions. Surgery may be necessary in more serious situations.
It's common to develop a lump or swelling in the anal area, known as a pile. They result from a buildup of blood vessels and tissue in the anal region. Internal and exterior piles are also possible.
Piles on the inside of the body are often painless but may lead to gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Pile formations on the skin are very uncomfortable and may cause itching, swelling, and even bleeding.
Video unavailable
This video is unavailable: Original link to video
Causes And Symptoms Of Piles
Hemorrhoids, or piles, are enlarged veins in the anus and rectum that cause pain and discomfort. They often cause distress and suffering. Nearly a third of the population will develop piles at some time in their life.
Inside and outside piles are the two main categories of heaps. Piles may be internal, found within the rectum, or external, found just below the skin surrounding the anus.
Pressure on the veins in the anal region is a common contributor of piles. Constipation, pregnancy, childbirth, obesity, and extended periods of sitting or standing are all potential causes. Piles may be caused by chronic diarrhea as well.
Pile symptoms include a tender or painful mass around the anus, itching or irritation around the anus, discomfort with bowel movements or sitting, and blood during bowel movements. An external hemorrhoid may become excruciatingly painful if a blood clot develops in it (thrombosed hemorrhoid). See a doctor if you have any of the symptoms associated with piles.
Treatment Options For Piles
Treatment options for piles, also known as hemorrhoids, depend on the type and severity of the condition. Here are some common treatments for piles:
- Over-the-counter creams and ointments:These can help reduce the swelling and discomfort associated with piles.
- Changes in diet and bowel habits:Increasing fiber intake, drinking plenty of water, and avoiding straining during bowel movements can help reduce the symptoms of piles.
- Warm baths:Sitting in a warm bath for 10-15 minutes can help relieve pain and discomfort associated with piles.
- Sitz baths:These are shallow baths that allow you to sit in warm water and can be especially helpful for reducing the pain and discomfort of external piles.
- Stool softeners:These can help make it easier to have bowel movements and reduce straining, which can help prevent the development of piles.
- Surgery:In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the piles.
It is important to consult with a doctor to determine the best course of treatment for your specific case of piles. Your doctor may recommend a combination of these treatments to provide relief.
Homeopathy Treatment For Piles
Homeopathy is a medical practice that treats the individual as a whole, rather than merely the signs and symptoms of illness. In the case of piles, homeopathic treatments are not only mild but also very successful.
People have conflicting views on the efficacy of homeopathy for piles, with some vouching for its use and others being skeptical. Homeopathy, on the other hand, seems to be a viable option for treating piles, particularly when combined with other therapies like dietary and behavioral modifications.
Some individuals claim that homeopathy entirely healed their piles, while many others report significant improvement. Some people find that it significantly lessens the intensity of their piles symptoms, making them much easier to deal with. It is possible that some individuals may experience no change at all after taking homeopathic treatments, although this is quite unusual.
If you want to try homeopathy for your piles but are unsure which remedies might be most effective for you, it's best to see a professional homeopath. Although homeopathic treatments are non-toxic and mild, they must be administered by a trained physician.
Prevention Of Piles
Preventing piles, also known as hemorrhoids, can help reduce the risk of developing the condition. Here are some tips for preventing piles:
- Eat a high-fiber diet:Incorporating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your diet can help prevent constipation, which can lead to the development of piles.
- Drink plenty of water: Staying hydrated can help prevent constipation and reduce the risk of piles.
- Avoid prolonged sitting:Prolonged sitting can put pressure on the veins in the anus and rectum, which can contribute to the development of piles.
- Exercise regularly:Regular physical activity can help reduce the risk of piles by improving bowel regularity and reducing the pressure on the veins in the anus and rectum.
- Avoid straining during bowel movements:Straining during bowel movements can increase the pressure on the veins in the anus and rectum, leading to the development of piles.
- Maintain good hygiene:Keeping the anal area clean and dry can help prevent infection and reduce the risk of developing piles.
- Avoid heavy lifting:Lifting heavy objects can increase the pressure on the veins in the anus and rectum, leading to the development of piles.
By following these tips and speaking with a doctor about your risk of piles, you can take steps to prevent the development of this condition.
People Also Ask
What Causes Piles?
The causes of piles can include straining during bowel movements, prolonged sitting, pregnancy, chronic constipation or diarrhea, a low-fiber diet, aging, and genetics.
What Are The Symptoms Of Piles?
The symptoms of piles can include pain or discomfort in the anus, itching in the anus, bright red blood in the stool, swelling or a lump near the anus, and pain during bowel movements.
How Are Piles Treated?
The treatment of piles can include over-the-counter creams and ointments, changes in diet and bowel habits, increased fiber intake, stool softeners, warm baths, sitz baths, and surgery for severe cases.
Final Words
While piles can be uncomfortable and even painful, they can often be treated with over-the-counter creams, changes in diet and bowel habits, and other self-care measures. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to provide relief.
It is important to speak with a doctor if you suspect that you may have piles, as they can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend the best course of treatment for you. Taking care of your body, including proper hygiene and a healthy lifestyle, can also help prevent the development of piles.

Stefano Mclaughlin
Author
Stefano Mclaughlin is a Psychologist focused on mental health, emotional well-being, and healthcare policy. He studied Psychology and Public Health at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, gaining a deep understanding of the intersection between mental health and public policy.
Stefano's mission is clear: he aims to destigmatize mental health discussions, improve access to mental healthcare, and promote emotional well-being for all. Drawing from personal experiences with anxiety and depression, Stefano shares real stories to make mental health topics more relatable and less intimidating.
In addition to his advocacy work, Stefano enjoys delving into books, experimenting in the kitchen, and embarking on new adventures. These hobbies fuel his creativity and inspire fresh perspectives for his advocacy work.

Dexter Cooke
Reviewer
Dexter Cooke is an economist, marketing strategist, and orthopedic surgeon with over 20 years of experience crafting compelling narratives that resonate worldwide.
He holds a Journalism degree from Columbia University, an Economics background from Yale University, and a medical degree with a postdoctoral fellowship in orthopedic medicine from the Medical University of South Carolina.
Dexter’s insights into media, economics, and marketing shine through his prolific contributions to respected publications and advisory roles for influential organizations.
As an orthopedic surgeon specializing in minimally invasive knee replacement surgery and laparoscopic procedures, Dexter prioritizes patient care above all.
Outside his professional pursuits, Dexter enjoys collecting vintage watches, studying ancient civilizations, learning about astronomy, and participating in charity runs.
Latest Articles
Popular Articles