Understanding The Zero Trust Security Model
The zero trust security model, a revolutionary approach to cybersecurity, challenges the conventional notion of trusting entities within a network perimeter. This article delves into the principles, benefits, and implementation strategies of the Zero Trust model.
Author:Tyreece BauerReviewer:Anderson PattersonFeb 07, 202434.6K Shares844.9K Views

In an era of increasing cyber threats, traditional security paradigms are proving inadequate to safeguard organizations against sophisticated attacks. The Zero Trust Security Model, a revolutionary approach to cybersecurity, challenges the conventional notion of trusting entities within a network perimeter. This article delves into the principles, benefits, and implementation strategies of the Zero Trust model.
Zero Trust Security - A Transformative Approach
Zero Trust Security is a cybersecurity model that demands strict identity verification for every person and device attempting to access resources within a private network, irrespective of their location within or outside the network perimeter. Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is the primary technology associated with the Zero Trust architecture, but it embodies a holistic approach to network security, incorporating various principles and technologies.
Core Principles
In simple terms, while traditional network security trusts anything within the network, the Zero Trust architecture adopts the principle of "never trust, always verify." This means that no user or device is automatically considered trustworthy, even if they are within the network perimeter.
Traditional network security relies on a defensive perimeter. It makes external access challenging, but once a malicious actor infiltrates, they gain considerable freedom of movement within the network. This is a critical point that Zero Trust proactively addresses.
Central Technology: ZTNA
Zero Trust Network Access(ZTNA) stands out as the key technology associated with the Zero Trust architecture. This technology facilitates continuous identity verification and the application of access policies as users and devices interact with the network. Multifactor authentication (MFA) and user behavior analysis are crucial components to ensure legitimacy at all times.
Understanding The Mechanism Of Zero Trust
Zero Trust operates on a sophisticated framework that amalgamates cutting-edge technologies to redefine the traditional approach to cybersecurity. This proactive model employs a combination of advanced tools, including risk-based multi-factor authentication, identity protection, next-generation endpoint security, and robust cloud workload technology.
Advanced Authentication Technologies
Zero Trust places a heavy emphasis on authentication by employing risk-based multi-factor authentication. This means that users or systems attempting to access resources undergo a rigorous authentication process that considers various risk factors. Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple means, reducing the likelihood of unauthorized access.
Identity Protection
Identity protection is a core component of the Zero Trust framework. It involves continuous monitoring of user and system identities to detect and respond to any suspicious activities. By constantly verifying the legitimacy of identities, Zero Trust ensures that only authorized entities gain access to the network and its resources.
Next-Generation Endpoint Security
To bolster the security of devices connected to the network, Zero Trust incorporates next-generation endpoint security solutions. This involves utilizing advanced threat detection mechanisms, behavioral analysis, and real-time monitoring to identify and mitigate potential security threats at the endpoint level.
Cloud Workload Technology
In the era of cloud computing, Zero Trust extends its protection to cloud workloads. Robust cloud workload technology is employed to secure applications and data hosted in the cloud. This ensures that, regardless of the location of resources, the same stringent security measures are applied, upholding the Zero Trust principles.
Dynamic Access Consideration
Zero Trust redefines access considerations by moving away from the traditional model of granting access based on static credentials. Instead, access is determined dynamically, considering various factors such as the user's behavior, device health, and the current security posture. This dynamic approach ensures that access privileges are continuously evaluated and adjusted in real-time.
System Security Maintenance
Maintaining the security of systems is a constant endeavor in the Zero Trust framework. Regular security updates, patches, and configuration reviews are essential to ensure that vulnerabilities are promptly addressed. This proactive maintenance approach helps in reducing the attack surface and fortifying the overall security posture.
Encryption Of Data
Data security is a paramount concern, and Zero Trust addresses this by emphasizing the encryption of sensitive information. All communication between users, devices, and applications is encrypted, adding an extra layer of protection against eavesdropping and unauthorized access.
Email Security
Securing email communication is integral to the Zero Trust model. By implementing robust email security measures, organizations can prevent phishing attacks, malware infections, and unauthorized access through compromised email channels.
Asset And Endpoint Hygiene
Before connecting to applications and the network, Zero Trust mandates the verification of the hygiene of assets and endpoints. This involves ensuring that devices are up-to-date with security patches, free from malware, and compliant with security policies before they are granted access.
Unlocking The Advantages Of Zero Trust
Fortifying Security Posture
Embracing the philosophy of "never trust, always verify," Zero Trust introduces a paradigm shift that significantly bolsters an organization's security posture. By relinquishing the traditional assumption of inherent trust, Zero Trust becomes a formidable defense mechanism against cyber threats. This model minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and lateral movement within the network, posing a formidable challenge for potential attackers attempting to navigate through the organization's digital infrastructure.
Key Highlights:
- Risk Mitigation:Zero Trust actively works to mitigate risks associated with unauthorized access, reducing the likelihood of successful cyber attacks.
- Lateral Movement Restriction:The model's design limits lateral movement, preventing threats from spreading freely within the network and minimizing potential damage.
Empowering Incident Response
Zero Trust not only fortifies preventive measures but also enhances the organization's incident response capabilities. In the unfortunate event of a security incident, the segmented nature of the network proves invaluable. This segmentation enables organizations to swiftly and effectively respond to incidents by containing and isolating threats. By compartmentalizing the impact of a potential breach, Zero Trust minimizes the overall damage and accelerates the remediation process.
Key Advantages
- Swift Containment:The segmented network allows for the swift containment of threats, preventing them from spreading across the organization.
- Isolation Strategies:Zero Trust supports effective isolation strategies, limiting the impact of security incidents and reducing the potential for widespread compromise.
Adapting To Modern Work Environments
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern work environments, characterized by remote work and cloud services, Zero Trust emerges as an adaptable and resilient security framework. Traditional security models are often bound by physical boundaries, making them less effective in a world where users and devices operate beyond conventional limits. Zero Trust, however, transcends these limitations, offering a robust security infrastructure that extends protection to users and devices, irrespective of their geographical location.
Key Features
- Remote Work Support:Zero Trust seamlessly supports the increasing trend of remote work, ensuring secure access regardless of the user's physical location.
- Cloud Service Integration:The model seamlessly integrates with cloud services, providing a consistent and comprehensive security approach that extends to cloud-based resources.
Navigating Challenges And Considerations In Zero Trust Implementation
Cultural Shifts
One of the primary challenges organizations encounter when adopting the Zero Trust model is the necessity for a cultural shift. Moving from a traditional trust-centric approach to a Zero Trust mindset requires a fundamental change in how employees perceive and interact with security.
This shift involves challenging long-standing assumptions about internal trust and advocating for a continuous verification mindset. Overcoming cultural resistance demands effective communication, training programs, and leadership support to ensure everyone is aligned with the new security paradigm.
Strategies For Overcoming Cultural Shifts
- Education and Training:Implement comprehensive training programs to educate employees about the principles and benefits of Zero Trust.
- Clear Communication:Transparently communicate the reasons behind the shift, emphasizing the shared responsibility of security among all members of the organization.
- Leadership Endorsement:Obtain visible support from leadership to reinforce the importance of the cultural shift.
Resource Allocation - Investing In Security Infrastructure
Implementing Zero Trust may necessitate significant investments in both technology and human resources. Organizations must allocate resources for deploying advanced security solutions, conducting thorough risk assessments, and implementing ongoing monitoring mechanisms. This shift in resource allocation can be challenging, especially for organizations with pre-existing security infrastructure. Successfully overcoming this challenge requires meticulous planning, a clear understanding of resource requirements, and prioritizing investments based on risk assessments.
Strategies For Effective Resource Allocation
- Comprehensive Risk Assessment:Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify critical areas requiring immediate attention and allocate resources accordingly.
- Prioritization Based on Risk:Prioritize resource allocation based on the criticality of assets and potential security threats.
- Scalable Solutions:Invest in scalable security solutions that can adapt to the evolving needs of the organization.
Resistance To Change - Overcoming Inertia
Resistance to change is a common challenge in any organizational transformation, and the adoption of the Zero Trust model is no exception. Employees and stakeholders may resist the shift due to concerns about increased complexity, perceived inconvenience, or fear of disruptions to established workflows. Addressing this resistance requires a combination of change management strategies, regular communication, and showcasing the tangible benefits of Zero Trust to ease apprehensions.
Strategies For Overcoming Resistance To Change
- Change Management Plans:Develop comprehensive change management plans to address concerns and anxieties among employees.
- Pilot Programs:Initiate small-scale pilot programs to demonstrate the positive impact of Zero Trust in controlled environments.
- Continuous Communication:Maintain open and continuous communication channels to address questions and concerns throughout the implementation process.
Commitment From Leadership - Setting The Tone For Zero Trust Adoption
Perhaps the most crucial factor in successfully navigating the challenges associated with Zero Trust implementation is securing commitment from organizational leadership. Leadership endorsement provides the necessary authority, resources, and momentum for the transition to a Zero Trust model. Without leadership commitment, overcoming cultural shifts, allocating resources, and addressing resistance to change become significantly more challenging.
Strategies For Securing Leadership Commitment
- Education and Awareness:Ensure that leadership understands the significance of Zero Trust by providing educational materials, case studies, and expert insights.
- Align with Organizational Goals:Demonstrate how Zero Trust aligns with broader organizational goals, emphasizing the positive impact on security and resilience.
- Establishing a Clear Roadmap:Develop a well-defined roadmap for gradual adoption, highlighting milestones and showcasing the benefits of each phase.
Zero Trust Security Model - FAQs
What Is The Concept Of Zero Trust Model?
The Zero Trust model is a cybersecurity paradigm that challenges the traditional notion of implicitly trusting entities within a network perimeter. In a Zero Trust framework, trust is never assumed, and every user, device, or application attempting to access resources is subjected to continuous verificationas a way to ensure security. This approach is based on the principle of "never trust, always verify." Regardless of the location, whether inside or outside the network, entities must continually authenticate and prove their legitimacy, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and lateral movement within the network.
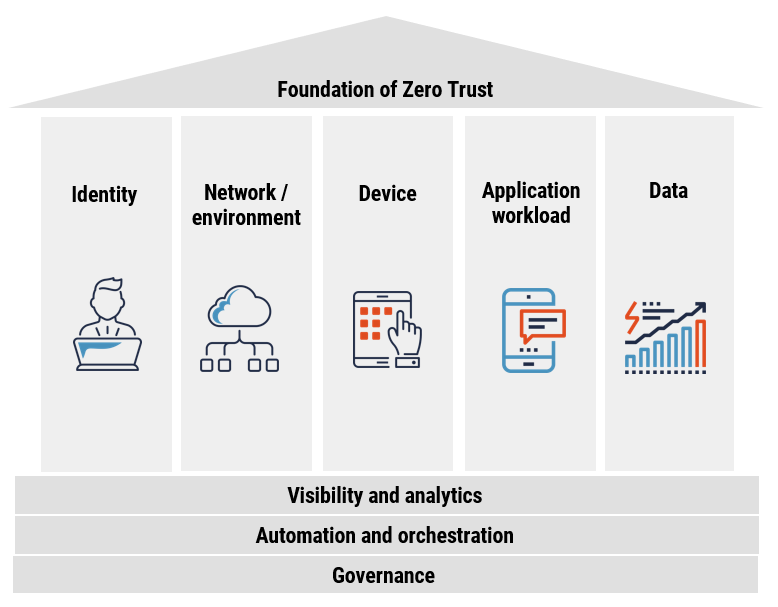
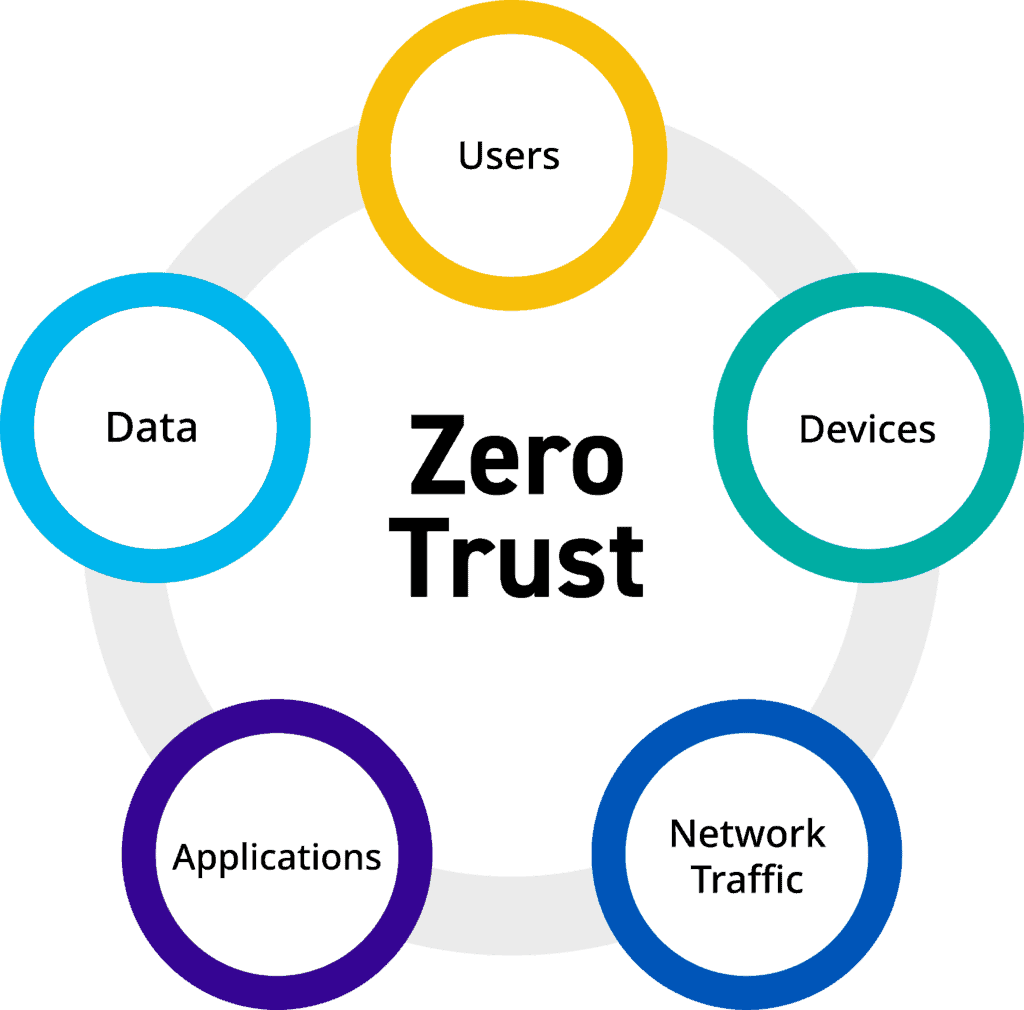
What Are The 5 Pillars Of Zero Trust?
The Zero Trust model is often structured around five core pillars, each contributing to the overall security posture. These pillars are:
Verify Identity
Continuous authentication ensures that users and devices are verified throughout their interaction with the network, reducing the reliance on static credentials.
Least Privilege Access
Access privileges are assigned based on the principle of least privilege, meaning users and devices are granted only the minimum permissions necessary to perform their specific tasks.
Micro-Segmentation
The network is divided into smaller, isolated segments to limit lateral movement in the event of a security breach, containing and isolating potential threats.
Assume Breach
Zero Trust assumes that threats may already exist within the network, prompting a proactive stance in continuously monitoring and responding to potential security incidents.
Encrypt Everything
Data is encrypted to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of information, even if it falls into the wrong hands. Encryption is applied to communications between users, devices, and applications.
What Are The Principles Of Zero Trust Security Model?
The principles that underpin the Zero Trust Security Model include:
Never Trust, Always Verify
The fundamental principle of Zero Trust revolves around not automatically trusting any user, device, or application, regardless of their location within or outside the network.
Continuous Authentication
Authentication is an ongoing process rather than a one-time event. Users and devices must continually prove their identity and compliance with security policies.
Least Privilege Access
Access rights are granted based on the minimum level required for specific roles or tasks, reducing the potential for misuse or abuse of privileges.
Micro-Segmentation
The network is segmented into smaller zones, allowing organizations to apply specific access controls, limiting the lateral movement of threats and containing potential breaches.
Assume Breach And Verify Hygiene
Zero Trust assumes that threats could be present and focuses on continuous monitoring and verification of the security hygiene of assets and endpoints.
Conclusion
The Zero Trust Security Model represents a paradigm shift in cybersecurity, offering a proactive and adaptive approach to safeguarding digital assets. By embracing the principles of least privilege, micro-segmentation, continuous authentication, and device trustworthiness assessment, organizations can significantly enhance their security posture in the face of evolving cyber threats. While the implementation may pose challenges, the long-term benefits make the adoption of Zero Trust a worthwhile investment in the defense against modern cyber threats.
Jump to
Zero Trust Security - A Transformative Approach
Understanding The Mechanism Of Zero Trust
Unlocking The Advantages Of Zero Trust
Navigating Challenges And Considerations In Zero Trust Implementation
Resource Allocation - Investing In Security Infrastructure
Resistance To Change - Overcoming Inertia
Commitment From Leadership - Setting The Tone For Zero Trust Adoption
Zero Trust Security Model - FAQs
Conclusion

Tyreece Bauer
Author
A trendsetter in the world of digital nomad living, Tyreece Bauer excels in Travel and Cybersecurity. He holds a Bachelor's degree in Computer Science from MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) and is a certified Cybersecurity professional.
As a Digital Nomad, he combines his passion for exploring new destinations with his expertise in ensuring digital security on the go. Tyreece's background includes extensive experience in travel technology, data privacy, and risk management in the travel industry.
He is known for his innovative approach to securing digital systems and protecting sensitive information for travelers and travel companies alike. Tyreece's expertise in cybersecurity for mobile apps, IoT devices, and remote work environments makes him a trusted advisor in the digital nomad community.
Tyreece enjoys documenting his adventures, sharing insights on staying secure while traveling and contributing to the digital nomad lifestyle community.

Anderson Patterson
Reviewer
Anderson Patterson, a tech enthusiast with a degree in Computer Science from Stanford University, has over 5 years of experience in this industry.
Anderson's articles are known for their informative style, providing insights into the latest tech trends, scientific discoveries, and entertainment news.
Anderson Patterson's hobbies include exploring Crypto, photography, hiking, and reading.
Anderson Patterson's hobbies include exploring Crypto, photography, hiking, and reading.
In the Crypto niche, Anderson actively researches and analyzes cryptocurrency trends, writes informative articles about blockchain technology, and engages with different communities to stay updated on the latest developments and opportunities.
Latest Articles
Popular Articles