How Blockchain In Global Trade Reshaping - Revolutionizing International Commerce
Unlocking the Future of blockchain in global trade - Discover how blockchain technology is revolutionizing international commerce, ensuring transparency, security, and efficiency.
Author:Anderson PattersonReviewer:Gordon DickersonFeb 12, 20244.8K Shares76.5K Views
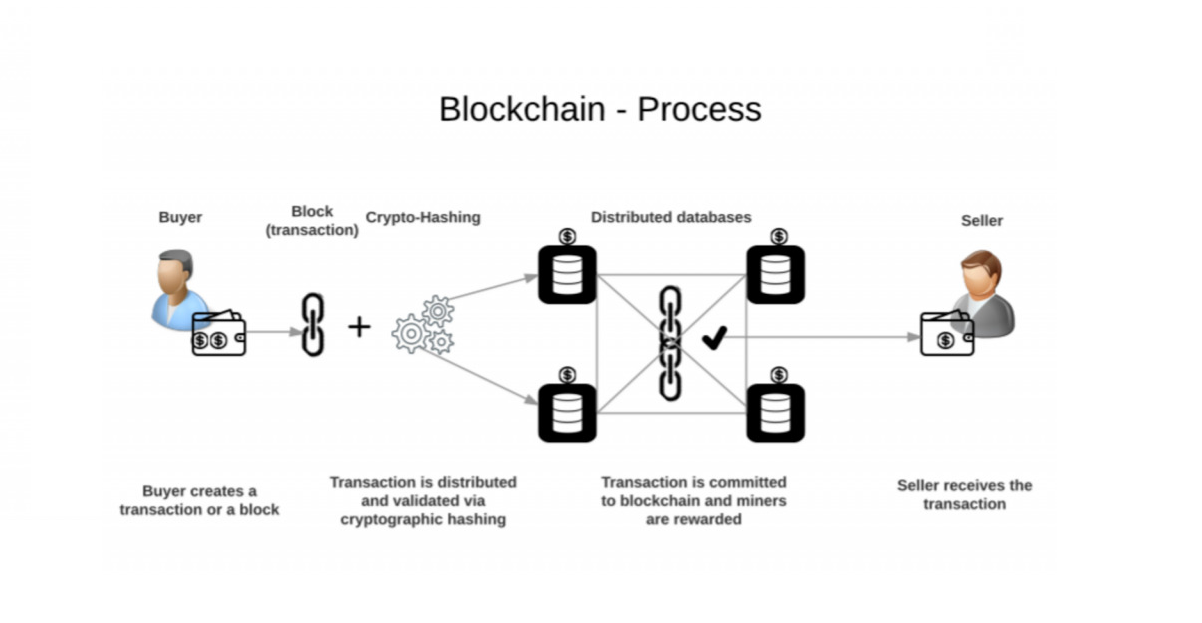
In the ever-evolving landscape of Blockchain in global trade, one technology stands out as a game-changer, With its decentralized ledger system and cryptographic security features, blockchain is revolutionizing the way businesses conduct transactions across borders. Imagine a world where every step of the supply chain is transparent, immutable, and instantly verifiable. That's the promise of blockchain in global trade.
Moreover, blockchain is breaking down barriers to entry for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), providing them with access to global markets like never before. By eliminating intermediaries and reducing transaction costs, blockchain levels the playing field and empowers entrepreneurs worldwide. In essence, blockchain isn't just transforming global trade.
10 Game-Changing Ways Blockchain Transforms
1. Empowering The Individual
Blockchain empowers individuals by giving them more control over their financial assets and eliminating reliance on centralized institutions. This fosters financial inclusion and promotes a more open and accessible financial system.
2. Enhanced Compliance
Blockchain technology can support regulatory compliance by providing auditable transaction records and automating Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) checks.
3. Tokenization Of Real-World Assets
Blockchain allows for the tokenization of real-world assets like real estate, art, and commodities, facilitating easier investment and fractional ownership for a wider audience.
4. Improved Market Discovery
Blockchain-based decentralized exchanges (DEXes) offer transparency in order book data and pricing, fostering fairer market discovery and reducing manipulation opportunities.
5. 24/7 Global Market
Unlike traditional markets with limited operating hours, crypto markets on blockchain operate continuously, offering greater flexibility and accessibility for global investors.
6. Programmable Contracts
Smart contracts automate trade execution based on predefined conditions, removing human error and emotional biases. This enables algorithmic trading strategies and ensures precise execution of complex orders.
7. Fractional Ownership:
Blockchain facilitates the fractional ownership of digital assets like cryptocurrencies and NFTs. This allows investors with smaller budgets to participate in previously inaccessible markets and diversify their portfolios.
8. Reduced Costs
Eliminating intermediaries within the blockchain network decreases transaction fees, making crypto trading more affordable for everyone. This democratizes access to the market and fosters wider participation.
9. Faster Settlements
Compared to traditional financial systems, blockchain enables near-instantaneous settlement of trades, improving efficiency and liquidity. This allows for quicker access to funds and faster execution of strategies.
10. Enhanced Security
Blockchain technology provides an immutable ledger, making transactions tamper-proof and reducing fraud risks significantly. This fosters trust and transparency in the market, attracting more participants.
What Are Some Potential Applications Of Blockchain In Global Trade?
Blockchain technology, with its inherent attributes of immutability, transparency, and security, opens doors for various innovative applications in global trade. Here are some key areas where it has the potential to revolutionize:
1. Trade Finance
- Streamlining transactions -Trade finance processes can be made faster and more efficient by eliminating paperwork and delays associated with traditional intermediaries. Blockchain platforms can automate document verification, payment processing, and trade finance procedures, reducing costs and increasing access to financing for all involved parties.
- Reducing fraud and errors -Blockchain's immutable ledger ensures the authenticity and security of trade documents, mitigating risks of fraud and errors. This builds trust and reduces disputes within the trade ecosystem.
2. Supply Chain Management
- Tracking goods and materials - Blockchain enables detailed tracking of goods and materials throughout the supply chain, providing real-time visibility and transparency. This improves efficiency, reduces theft and counterfeiting, and facilitates collaboration between stakeholders.
- Ensuring product quality and origin -Blockchain-based platforms can store and share quality certifications, origin certificates, and other relevant data. This empowers consumers to make informed choices and holds producers accountable for ethical sourcing and sustainable practices.
3. Securities And Asset Trading
- Fractional ownership:Blockchain facilitates fractional ownership of assets like real estate, art, and commodities, making such investments more accessible to a wider audience with smaller capital. This diversifies the investor base and promotes liquidity in previously illiquid markets.
- Streamlined trading and settlement:Blockchain platforms can automate securities trading and settlement processes, eliminating traditional intermediaries and speeding up transactions. This reduces costs and increases efficiency for investors and issuers.
4. Intellectual Property Rights Management
- Protecting and verifying ownership -Blockchain provides a secure and transparent way to register and transfer intellectual property rights, preventing unauthorized use and facilitating royalty payments.
- Combating counterfeiting -Blockchain-based solutions can help track and identify counterfeit goods, protecting brands and consumers.
What Are The Challenges Of Using Blockchain In Global Crypto Trade?
Despite its potential, blockchain technology faces several challenges when it comes to widespread adoption in global crypto trade. Here are some key hurdles:
1. Regulation and legal uncertainty - The regulatory landscape surrounding crypto and blockchain is still evolving, creating uncertainty for businesses and investors. Different jurisdictions have varying regulations, making it difficult for platforms to operate globally. Lack of clarity around legal definitions and classifications of crypto assets adds to the challenge.
2. Scalability and performance - Existing blockchain platforms often struggle to handle the volume and speed required for large-scale global trade. Transaction processing times can be slow, and fees can be high, particularly during peak periods. Scaling solutions like Layer 2 technologies are emerging, but their long-term effectiveness remains to be seen.
3. Security vulnerabilities - While blockchain offers inherent security through its consensus mechanisms, vulnerabilities exist in smart contracts and protocols. Hacks and exploits can result in significant financial losses, undermining trust and confidence in the system. Enhancing security measures and conducting thorough audits are crucial.
4. User adoption and education - Widespread adoption requires greater public understanding and education about crypto and blockchain technology. Many individuals remain unfamiliar with the concepts and hesitant to participate due to perceived risks and complexities. Educational initiatives and user-friendly interfaces are essential to bridge the knowledge gap.
5. Energy consumption -Some proof-of-work consensus mechanisms used in blockchain can be energy-intensive, raising environmental concerns. Sustainable solutions such as proof-of-stake protocols and alternative consensus mechanisms are being explored, but their widespread adoption is still underway.
6. Interoperability and fragmentation -Different blockchain platforms operate with varying protocols and standards, creating interoperability challenges. Seamless communication and asset transfer between different networks are required for a truly global market, and cross-chain solutions are evolving to address this issue.
7. Liquidity and market manipulation -While blockchain aims to increase transparency, issues like wash trading and pump-and-dump schemes can still occur. Building robust market surveillance mechanisms and fostering ethical trading practices are important to maintain market integrity.
8. Lack of skilled professionals -The growing demand for blockchain expertise outpaces the supply of qualified professionals. Educational programs and training initiatives are needed to equip individuals with the necessary skills to develop and maintain blockchain-based trading systems.
9. Decentralization vs. regulation -Finding the right balance between decentralization and regulatory oversight is crucial. While complete decentralization may face challenges in ensuring compliance and preventing illegal activities, overly restrictive regulations can stifle innovation and hinder adoption.
10. Infrastructure and technical complexity - Setting up and maintaining blockchain infrastructure requires technical expertise and resources that might not be readily available to all participants. Developing user-friendly and accessible tools can help overcome this barrier.
Are There Any Existing Examples Of Blockchain Used In Global Trade?
While cryptocurrencies themselves aren't directly involved in the physical movement of goods or materials in global trade, blockchain, the technology powering them, is finding its way into various aspects of global trade, even beyond simple financial transactions. Here are some existing examples:
- TradeLens - Developed by Maersk and IBM, TradeLens is a blockchain platform digitizing trade documentation and streamlining processes like customs clearance and payments.
- we.trade -Another trade finance platform powered by IBM and Deutsche Bank, we.trade allows small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to access trade finance solutions more easily and efficiently through blockchain technology.
- Provenance -This platform uses blockchain to track the origin, authenticity, and movement of food products across the supply chain.
- VeChain -VeChainblockchain platform focuses on supply chain management, tracking goods and materials across various industries like pharmaceuticals, luxury goods, and agriculture.
- tZERO -This platform utilizes blockchain for trading tokenized securities, including stocks and bonds.
- Globacap - Developed by Societe Generale, Globacapis a blockchain platform for trading tokenized securities and other financial assets.
FAQ's About Blockchain In Global Trade
How Is Blockchain Used In Trading?
It is best known for its association with the cryptocurrency Bitcoin, but it can be used in any process involving transactions and exchanging data. Blockchain works by verifying and recording transaction data in a permanent way on a single, secure digital ledger shared by trusted counterparties.
Is Blockchain Used In Stock Market?
Mainly blockchain will help us to make optimal stock exchanges through automation and decentralization. Stock market across the globe is rapidly using blockchain technology for the market transaction.
Is Forex Trading A Blockchain?
Based on its success in the cryptocurrency market and some limited applications in other sectors, block chain technology is being actively considered for deployment in fixed income and forex (FX) trading.
Conclusion
The integration of blockchain technology into global trade represents a monumental shift in the way businesses operate and interact on a global scale. Its immutable ledger, decentralized structure, and cryptographic security have the potential to streamline processes, increase transparency, and reduce costs across the entire supply chain.
As blockchain continues to mature and gain widespread adoption, it will undoubtedly reshape the dynamics of international commerce, fostering trust and efficiency in transactions while opening doors for smaller players to participate more effectively in the global marketplace.

Anderson Patterson
Author
Anderson Patterson, a tech enthusiast with a degree in Computer Science from Stanford University, has over 5 years of experience in this industry.
Anderson's articles are known for their informative style, providing insights into the latest tech trends, scientific discoveries, and entertainment news.
Anderson Patterson's hobbies include exploring Crypto, photography, hiking, and reading.
Anderson Patterson's hobbies include exploring Crypto, photography, hiking, and reading.
In the Crypto niche, Anderson actively researches and analyzes cryptocurrency trends, writes informative articles about blockchain technology, and engages with different communities to stay updated on the latest developments and opportunities.

Gordon Dickerson
Reviewer
Gordon Dickerson, a visionary in Crypto, NFT, and Web3, brings over 10 years of expertise in blockchain technology.
With a Bachelor's in Computer Science from MIT and a Master's from Stanford, Gordon's strategic leadership has been instrumental in shaping global blockchain adoption. His commitment to inclusivity fosters a diverse ecosystem.
In his spare time, Gordon enjoys gourmet cooking, cycling, stargazing as an amateur astronomer, and exploring non-fiction literature.
His blend of expertise, credibility, and genuine passion for innovation makes him a trusted authority in decentralized technologies, driving impactful change with a personal touch.
Latest Articles
Popular Articles